FAQs about Climate Change

11. What would happen if climate change could not be stopped?
If the goal of reducing the global temperature to 2 ° C or less of its pre-industrial level is not achieved, this would have serious consequences for life on Earth. Depending on the magnitude of the warming, we could attend different events and even climatic catastrophes, such as the increase in the frequency and intensity of droughts, fires, desertification, floods, landslides, hurricanes, tornadoes and typhoons. The melting of the Poles would increase, which would increase the level of oceans and seas, affecting the coastal and island populations. There would be a shortage of food and drinking water, famines, deaths and massive exoduses never seen. The desertification of the Amazon would worsen, aggravating the greenhouse effect by damaging the lung of the Earth. When extinct quantities of species would affect biodiversity and food chains, with serious consequences for the biological balance of the planet. It would multiply the extinction of species and the uncontrolled reproduction of insects, bacteria and viruses with great danger for humans.
Other FAQs about Climate Change
1. What is climate change and what is its origin?
2. What are the causes of global warming?
3. What are the consequences of climate change?
4. Are there examples of recent climate changes on Earth?
5. Why and how much will sea level rise in the future?
6. What are glaciers, icefield and Arctic ice and why are they related to climate change?
7. Is permafrost a climatic weather bomb due to global warming?
8. How will climate change affect humans and other species in the future?
9. What is the role of mitigation, adaptation and resilience to climate change?
10. How can we lose the fight against climate change?
11. What would happen if climate change could not be stopped?
12. Why the Amazon rainforest is the lung of the world?
13. Is the Amazon forest in danger of disappearing?
14. Have we reached the Anthropocene?
Other sections of Climate Change

Pioneers of Climate Change
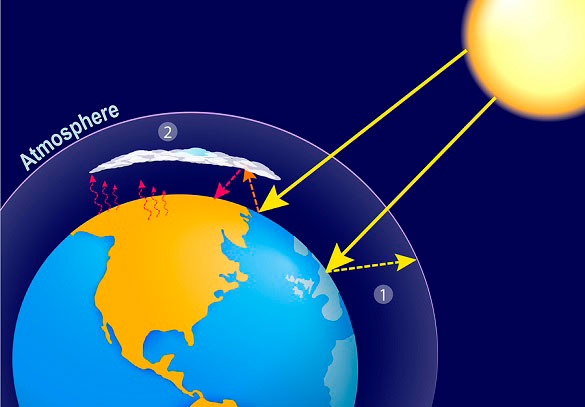
At all times and in all sciences, there have always been visionaries, those people who anticipate situations long before other persons can glimpse them. This is the case of Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830), a French mathematician and physicist, who in 1824 calculated that an object the size of the Earth and with a similar distance from the sun, it should be much colder to what our planet is really like. He affirmed that it was maintained with a temperate climate because the atmosphere retains the heat as if it were under glass. Thus, Fourier has the honor of being the first to use the greenhouse analogy…

Climate change, what is it and what are its causes?
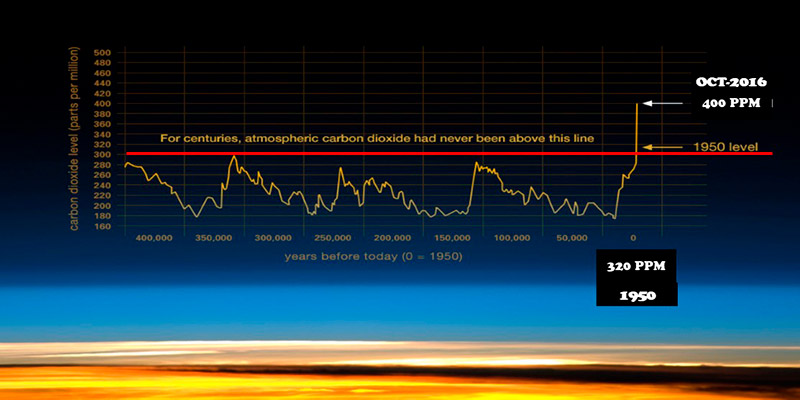
Anthropogenic climate change is the variation of climate status attributed to human activity that alters the composition of the atmosphere and has consequences on the entire planet. The main cause of climate change is global warming caused by emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG), of anthropogenic origin, among which CO2 is the most frequent. The sources responsible for these emissions are the burning of fossil fuels such as oil, coal and gas, used mainly in industry and transport.