FAQs about Desertification
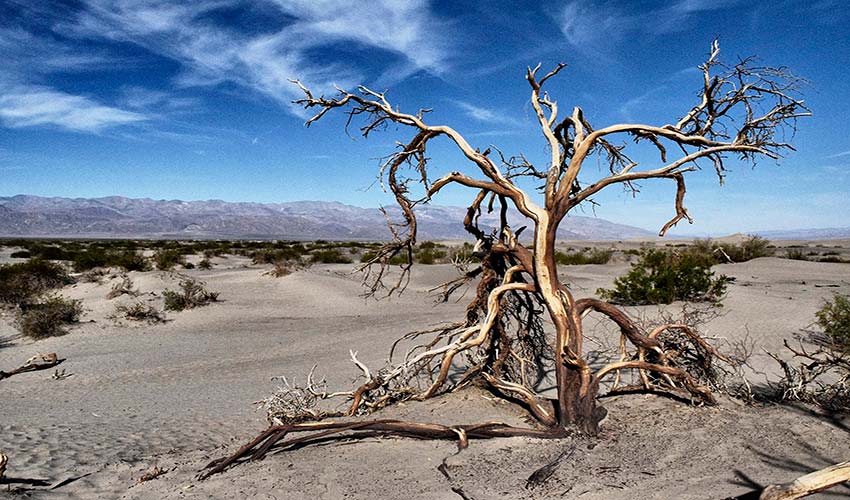

Source: Bummelhummel en Pixabay
6. What is the relationship between global warming and desertification?
The causes of anthropogenic global warming, that is, those caused by human activities, are largely due to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from burning fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil. Other causes correspond to deforestation of forests, the intensification of agriculture and the livestock industry.
All this has produced a constant increase in world temperature in the last two and a half centuries and has had adverse effects on the planet’s climate system, including soil desertification.
Desertification is one of the main environmental problems on Earth. Article 1 of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) defines desertification as “the degradation of dry, semi-arid and sub-humid lands resulting from various factors, such as climatic variations and human activities”.
Since the 1950s, and especially the 1970s, hostile deforestation of Earth’s main forests has been taking place. Despite the forest and desertification conventions that have been brought forward since 1992, deforestation is far from diminishing.
The best way to combat desertification, but the most difficult, would be by drastically reducing deforestation in the different forests of the planet.