FAQs about Desertification
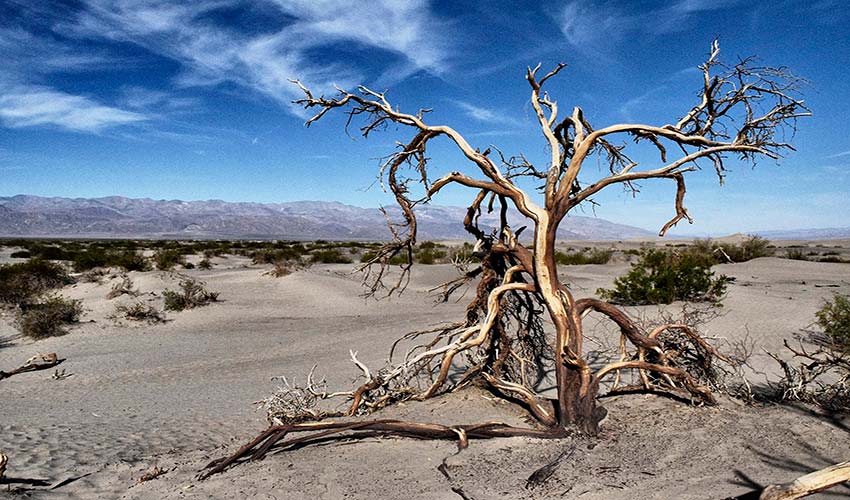

Source: Bummelhummel en Pixabay
4. What are the consequences of desertification?
If desertification is not stopped, its consequences will have a greater impact on the social, economic, and environmental aspects of the planet. We would see great imbalances in biodiversity, forest fires, droughts, crop losses, famines, mega migrations, critical shortages of drinking water in almost all regions of the globe.
Desertification also results in the loss of fertile soils and vegetation cover. Drylands contain significant amounts of carbon that could be released into the atmosphere as a consequence of desertification, with significant repercussions for the global climate system. Drylands are known to release millions of tons of CO2 into the atmosphere from desertification, which increases global warming.
Desertification is one of the most serious problems on Earth and difficult to solve. It is easier to change the internal combustion automotive traffic for electromobility than to end the deforestation of jungles and forests.
Even if greenhouse gas emissions are largely eliminated, but deforestation, and therefore desertification, cannot be stopped, the progressive elimination of vegetation cover and the loss of hundreds of ecosystems on Earth will continue. This process began in the 1950s and accelerated in the 1970s. Since then and to date it has not been possible to stop the growth process of arid, semi-arid and sub-humid lands.