7. How does fracking affect climate change?
Leading the world towards the massive use of energy of fossil origin, with contributions of new techniques such as fracking, is revitalized greenhouse gas emissions, which goes against the Paris Agreement. If fracking were generalized on the planet, this would put an end to the hopes of achieving the goal of increasing the world temperature by less than 2º C by the end of the century, in relation to its pre-industrial level. In the case of shale gas, which is between 90% and 95% methane, although it is true that its contribution to the greenhouse effect is 21 times greater than that of CO2, it must also be said that its participation in the atmosphere is 220 times smaller. According to climatic agreements reached, the use of greenhouse gases (GHG) must be reduced to zero by the end of the century. The discovery of unconventional deposits and the invention of new procedures to extract hydrocarbons entail serious difficulties in achieving this goal. Failing to do so could be catastrophic.
Other FAQs about Fracking
1. What is fracking?
2. What products are obtained with fracking?
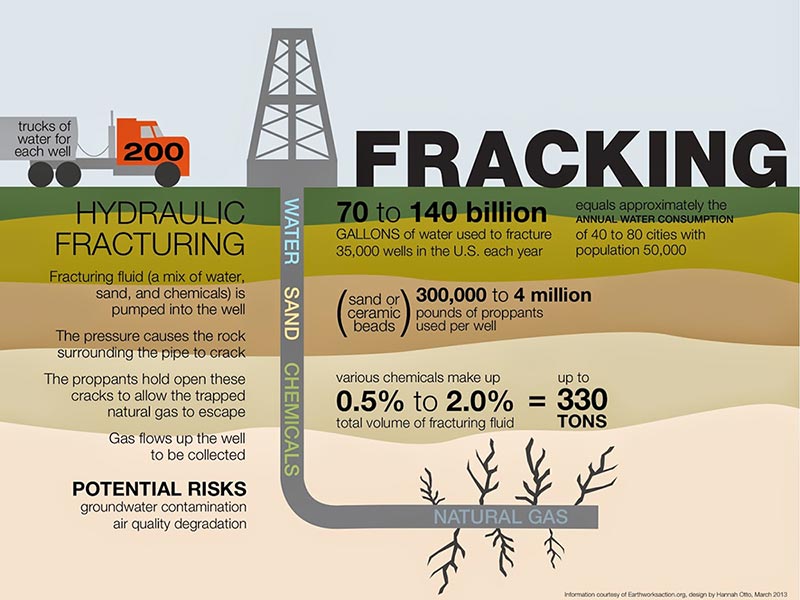
3. How is the fracking procedure?
4. When was fracking first used?
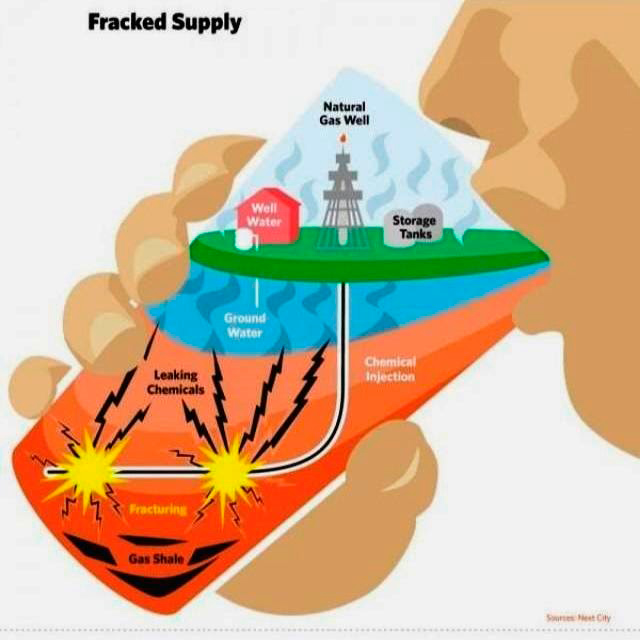
5. Is fracking dangerous?
6. How does fracking affect the environment?
7. How does fracking affect climate change?
8. What are shale gas and shale oil?
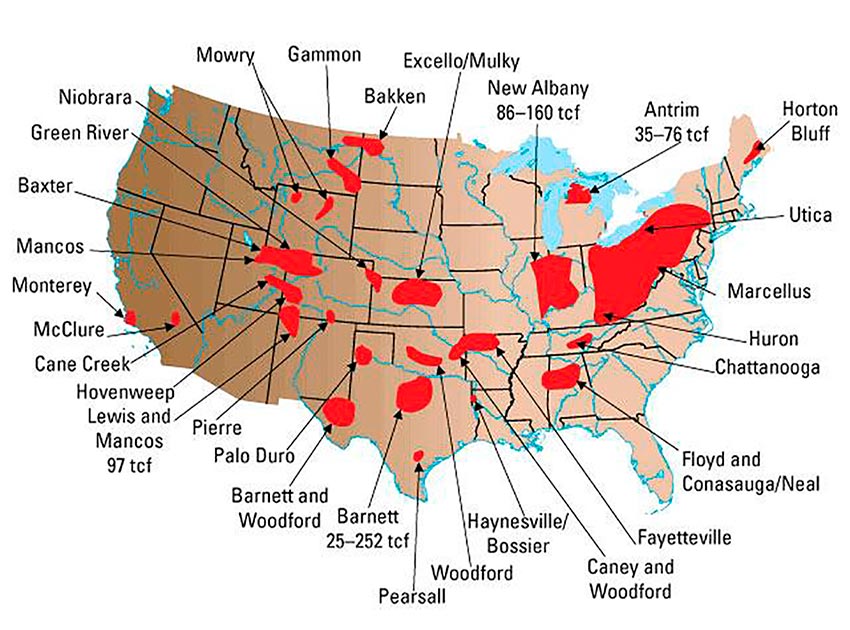
9. In what countries is fracking done?
10. Are there regulations for fracking technology?
11. In which countries is fracking prohibited?
Other sections of Fracking

Fracking fever, a real threat to Paris Agreement
The failure of the Paris Agreement would be the failure of Homo sapiens. If we do not reverse the increase in global warming and we do not support sustainability on our planet, we will all be losers. There are clear indications that we are going in a opposite direction to the 2015 agreements, as can be seen in this paper. The increasing fever of the fracking, due to the cheapening of the processes of extraction…

Fracking or hydraulic fracturing
Fracking, or hydraulic fracturing, is an unconventional method of extracting oil and gas that requires vertical and horizontal drilling at great depths. The first commercial hydraulic fracturing was achieved as recently as 1998. Fracking is a very controversial technology since it prolongs the use of fossil-fuel hydrocarbons…