FAQs about Global Warming

5. What must be done to stop global warming?
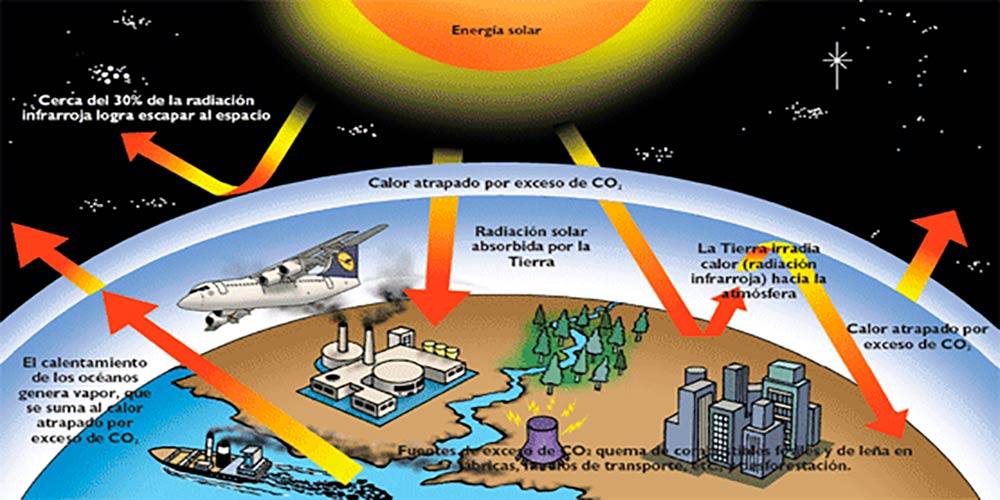
The Paris Agreement has as its main goal to limit the increase in global temperature to less than 2°C of its the end of this century. To mitigate climate change, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions must be progressively reduced until they are eliminated, especially those based on fossil fuels such as oil, gas and coal. GHG when burned release carbon dioxide (CO2) into atmosphere, causing increased global warming and climate change. To mitigate unwanted effects, fossil fuels must be replaced by clean or renewable energies, such as wind energy or solar energy, green cities, electric cars, etc. If the goal of 2°C is not reached, we could see the increase in the level of seas and oceans, with serious damage to the most vulnerable populations. Floods, landslides, hurricanes, tornadoes, forest fires and other catastrophic events, potentially more destructive than those now known, would also increase.
Other FAQ’s about Global Warming
1. What is global warming and how is it different from climate change?
2. What is the greenhouse effect and what are its consequences?
3. What have been the causes of global warming?
4. What are the consequences of global warming?
5. What must be done to stop global warming?
6. What does mitigation, adaptation and resilience mean to climate change?
7. Is it proven that global warming is caused by human beings?
8. What is the Anthropocene?
9. When and who spoke for the first time about global warming?
10. What were the first climate conferences in the world?
Other sections of Global Warming
Magazine
Natural global warming, key factor of life on Earth
Global warming is a natural phenomenon caused by the greenhouse effect, a special feature of the Earth’s atmosphere that has allowed the multiplication of life throughout the planet, through enormous biodiversity…