FAQs about Global Warming

6. What does mitigation, adaptation and resilience mean to climate change?
Mitigation. It is a term that means attenuate or soften a negative thing, such as a disease or a headache. In the case of global warming, mitigation refers to the reduction of emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) or fossil fuels until their total eradication. They also include the improvement of the sumps to increase the absorption capacity of this gases. Likewise, programs such as carbon taxes and incentives for voluntary GHG reduction and clean energy substitution are considered.
Adaptation. It refers to the actions that must be carried out to prevent changes that can produce undesired effects. In the case of global warming, adaptation refers to initiatives and measures that reduce the vulnerability of natural and human systems to climate change. Countries and communities must implement preventive actions and practices to avoid probable harm. Short and long-term actions must be contemplated, through environmental management, planning and disaster management.
Resilience It is the adaptation capacity of a living being to face a disturbing agent or an adverse state or situation. In the case of global warming and climate change, resilience refers to the capacity of an ecosystem to absorb disturbances, without significantly altering its structural and functional characteristics, and can return to its original state after the disturbance factor has ended. The societies that currently suffer consequences of climate change, such as frequent flooding, desertification of soils, air pollution in cities, respiratory and dermatological syndromes, are better prepared to withstand future environmental catastrophes. The Paris Agreement places special emphasis on increasing the capacity for adaptation, strengthening resilience and reducing vulnerability to climate change.
Others FAQ’s about Global Warming
1. What is global warming and how is it different from climate change?
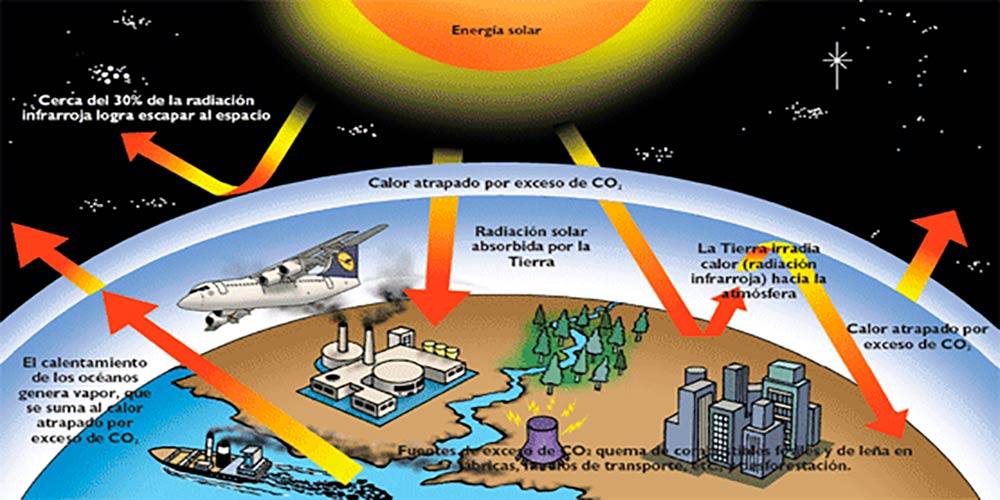
2. What is the greenhouse effect and what are its consequences?
3. What have been the causes of global warming?
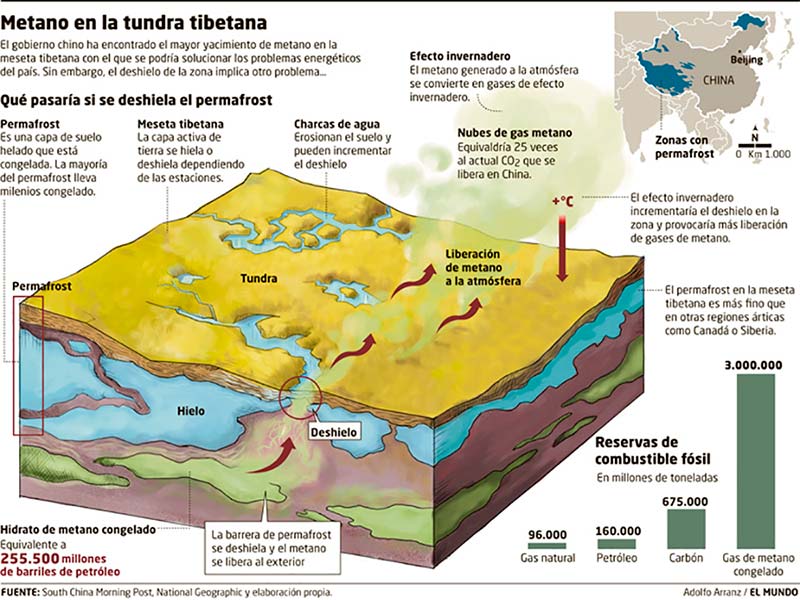
4. What are the consequences of global warming?
5. What must be done to stop global warming?
6. What does mitigation, adaptation and resilience mean to climate change?
7. Is it proven that global warming is caused by human beings?
8. What is the Anthropocene?
9. When and who spoke for the first time about global warming?
10. What were the first climate conferences in the world?
Other sections of Global Warming
Magazine
Natural global warming, key factor of life on Earth
Global warming is a natural phenomenon caused by the greenhouse effect, a special feature of the Earth’s atmosphere that has allowed the multiplication of life throughout the planet, through enormous biodiversity…