Magazine all about Soils
Origin, importance and degradation of soils
The origin of soils is closely related to the formation of the earth’s crust. After the cooling and hardening of the Earth’s surface, a process that lasted hundreds of millions of years, soils emerged. Its formation involved the mechanical dissolution of rocks, the incorporation of particles and substances from air and water, but above all the installation of living beings on the planet, almost from the beginning. Soils are mostly biologically active. Microfauna and microflora enrich the substrate, the medium in which plants fix and nourish themselves, through their depositions, secretions and other activities during their lives, or fermentation or putrefaction after their deaths.
The importance of soil today is that it is the main support of animal and plant life on the planet. In fact, humans live on land or islands, forests developed on soils and most animals currently live on land, even birds spend the night on the ground.
Since intensive agriculture appeared a century and a half ago, the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides and other agro-industrial methods have endangered soils. The consequences of soil contamination and degradation are serious. Few know that the speed of soil losses today is greater with which they are formed. There are already those who consider the soil as a non-renewable natural resource.
The process of formation of the earth’s crust

Artistic representation of the formation of the earth’s crust. Source: Geological Man – WordPress.com
The importance of soils
Soils are a fundamental factor in the proliferation of biodiversity on Earth. They are the main producer of food and support for animal and plant life on the planet. The soil is the support of the biological substrate, the medium or surface on which the plants and animals are fixed and nourished. Much of life develops on the ground. Humans live on land or islands. The forests obviously develop in the soil and most of the animals live on land, even birds spend the night in the ground.


Source: ecuador593erosion.blogspot.com
Degradation of soils
Since intensive agriculture appeared, a century and a half ago, their methods have endangered soils. The use of fertilizers, chemical pesticides and other agricole-industrial methods have caused their contamination and degradation. Few know that the speed of soil losses is currently greater with which they are formed. There are those who consider the soil as a non-renewable natural resource.
How are islands formed?
How are volcanoes formed?
The substrate and success of life on Earth
The biological substrate is the medium from which plants and animals are fixed and nourished. The soils are the main supporters of the substrate. The micro fauna and microflora enrich the substrate through depositions, secretions and other activities during their lives, or fermentation or putrefaction after their deaths. The substrate may include biotic or abiotic materials. For example, the substrate of an alga may be a rock to which it attaches itself, while the alga itself may be the substrate of another animal that lives on top of it.
The substrate explained without words

Source: fotos.miarroba.com

Clinging to life on a concrete substrate


Source: Pinterest.com
Life emerges almost
anywhere on Earth
________
Our planet is considered
by some to be the greatest
known living being
The soil is alive
Soil is a living organism

Fuente: SGK-PLANET
ONE: Soils emerged after the cooling and hardening of the Earth’s surface, a process that lasted hundreds of millions of years.
TWO: Soils are the main support of life on the planet. Humans, most other animals and vegetation cover live on land or on islands.
THREE: Pollution and degradation of soils are two serious problems. The loss of soils is currently greater with which they are formed. Some consider the soil as a non-renewable natural resource.
Continental drift, soil formation and biodiversity
The movement of the continents, these large containers of soils, substrates, water and life, played an important role in the formation of the great biodiversity existing on Earth. The evolution of the different shapes, sizes, colors, locomotion and distribution of species is partly due to continental drift, the name of the phenomenon through which the plates have been moving over liquid magma, over millions of years, from the Pangeia until its current distribution.
Pangeia
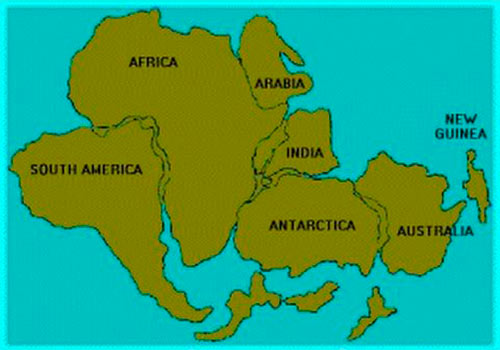
Source: Pinterest
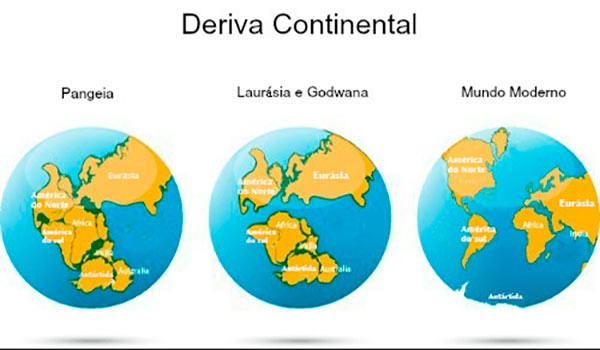
Source: danielaciencias.blogspot.com
Life is as tied to Earth as Earth is to life
The Earth is 4,700 million years old and microfossils have been found in rocks that are believed to date from 4.1 billion years ago in Australia, Greenland and South Africa. These are small structures only visible through the microscope. This shows that our planet almost from its inception was a carrier of life. Soil formation was and remains fundamental for the maintenance of biological diversity on the planet.

Source: ramanujan25449.blogspot.com
Australia
4100 MM years

Source: ramanujan25449.blogspot.com
Groenlandia
3.700 MM years

Source: Europa Press
Sudáfrica
2.400 MM years
Soil diversity
Soils also benefit from diversification on our planet. They are composed of superimposed levels or layers, which in each region have a different physical, chemical and biological peculiarity. This process gave rise to a great diversity of soils, among them the sandy, limy, silty, humiferous or black soil, clayey, stony, peat and saline. With this particularity, soils have been a fundamental factor in the proliferation of biodiversity existing on Earth.
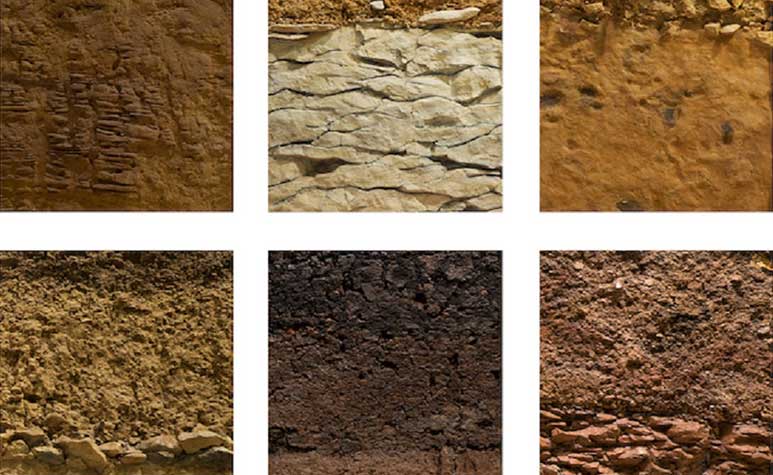

Source: Decoración y jardines
Diversity of products from the soil
Life emerges almost
anywhere on Earth
______
Our planet is considered
by some to be the
greatest known living being
_____
The soils have a
preponderant role in it

Three cereals that developed three civilizations



Causes and consequences of pollution and soil degradation

Causes of pollution
Pollution happens when certain elements that cause harmful effects accumulate in quantities that nature cannot recycle.
Chemical degradation of soils
It is mainly due to the excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides and phytosanitary agents, to irrigation with contaminated water and to the mishandling of garbage and other waste.
Physical degradation of soils
It is related to the deforestation of forests, the construction of roads, cities and other civil works. In these processes the elimination of habitats, micro fauna and microflora occurs and finally the degradation and death of the soil succeeds.
What is a pollutant?
A contaminant is a substance
that is found in a medium
to which it does not belong
or that does so at levels
that can cause adverse effects

Products and procedures that degrade soils
In soils we inject all kinds of substances, some very toxic and dangerous. Among them are fertilizers, pesticides, fumigants, solid waste, heavy metals, radioactive contaminants. Acid rains bring toxic substances and harmful products. We pollute agricultural and livestock lands, mining camps, plains, mountains, forests, beaches, glaciers, deserts and even our small gardens.

Damage caused by fumigation
The degradation of soils is due, among others, to the exaggerated use of pesticides or fumigants. These methods, in addition to eliminating pests and diseases, also produce the extinction of organic matter necessary to carry out the processes involved in the formation of humus, essential for the growth of plants, in extreme cases extinction can occur.
What are fertilizers? Its benefits and damages to the floors
A fertilizer is a chemical that is applied to soils to increase their fertility and regulate their acidity or alkalinity. Fertilizers contain nutrients assimilable by plants, to maintain or increase the content of these elements in the soil.

Source: Zootecnia y Veterinaria es mi pasión
Benefits of fertilizers
Fertilizers are used to improve the quality of the substrate and stimulate the growth of plants. Its main nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. There are other secondary components. Nitrogen contributes to the development of aerial parts of the plant. The phosphor reinforces the plants and contributes to the development of the root. Potassium helps to promote flowering and the development of fruits.
Damage of fertilizers to soils
The most frequent risk to health, due to the use of fertilizers, is the consumption of contaminated foods with a high nitrate content.
For the environment, the most common risk is the contamination of drinking water, due to fertilizers used in excessive amounts to improve impoverished soils. The risk is that the soluble elements reach the water table by infiltration, or to the water courses by drag.
Effects on soil fertility, structure, humus and biological activity.

Source: Software ERP Agrícola
What are phytosanitary products and how do they affect soils?
The phytosanitary product, pesticide or agrotoxic is defined, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) as that substance or mixture of substances intended to prevent, destroy, attract, repel or fight any pest or disease, or destroy directly, insects, mites, mollusks, rodents, fungi, weeds, bacteria and other forms of animal or vegetable life harmful to public health and also to soils and agriculture, that is, considered as pests and therefore susceptible to being combated with pesticides.

Source: albogarden.com
Consequences of mismanaged landfills
Waste dumps or landfills managed in an inappropriate manner have harmful consequences for soils and aquifers. Leaks from these spaces destined for the accumulation of garbage can cause serious consequences for the environment and therefore for the health of humans and nearby ecosystems.
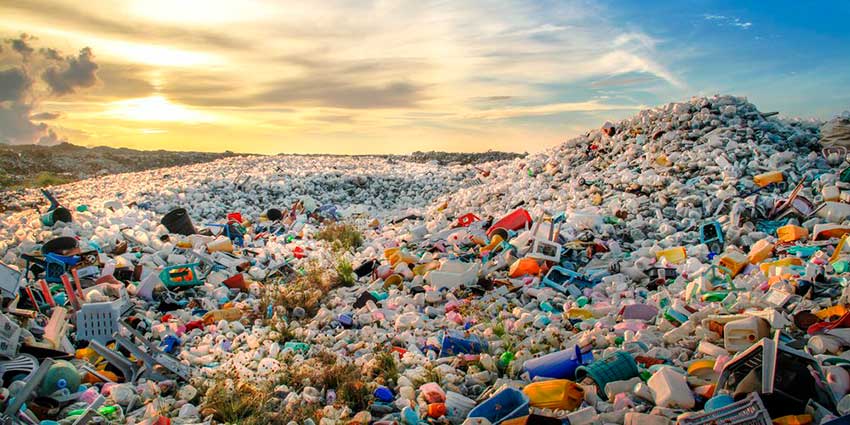

Source: Desechos-solidos.com
Recycling of waste
The three keys to waste recycling are: reduce, reuse and recycle. In this way waste is used to convert them into new products or raw materials for later use. The process has an important additional advantage, which is that the volumes of garbage are reduced and consequently the contamination of the environment, including the soil and aquifers.

Source: recytrans.com
Oil spills on the floors
La contaminación de suelos debido al derrame de hidrocarburos es bastante frecuente. Especialmente durante los procesos de producción de crudo, transporte, almacenamiento, comercialización y distribución. La contaminación por petróleo afecta la composición química y física de los suelos. La degradación del suelo puede concluir en su extinción en las áreas más afectadas.
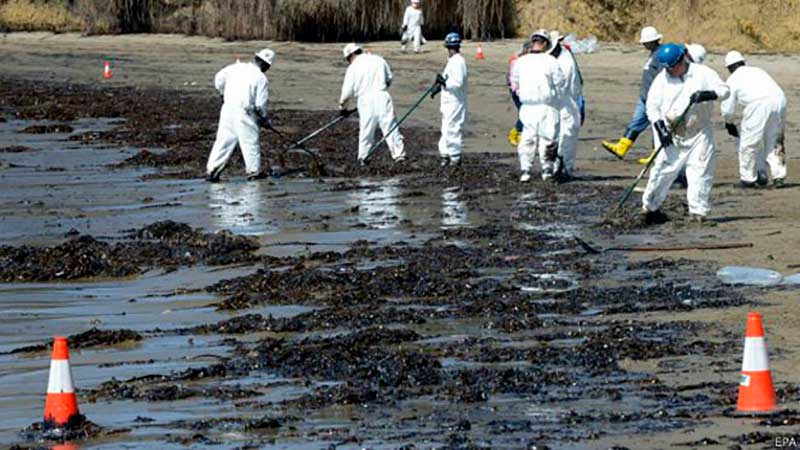

Source: teleradioamerica.com/vía BBCMundo
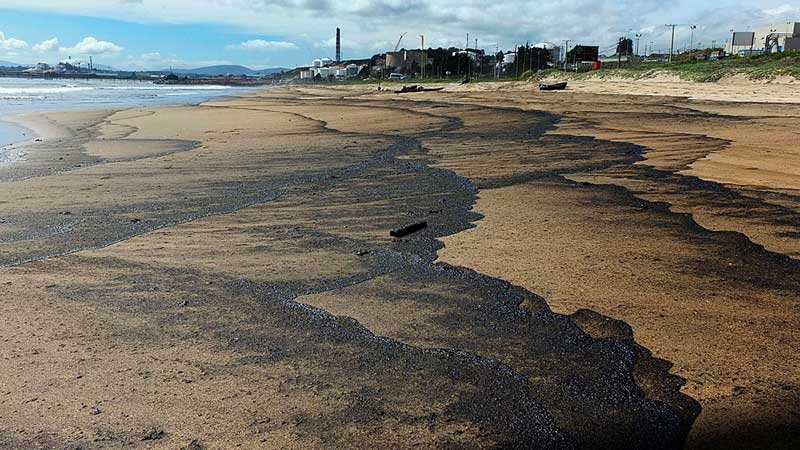

Source: publimetro.cl
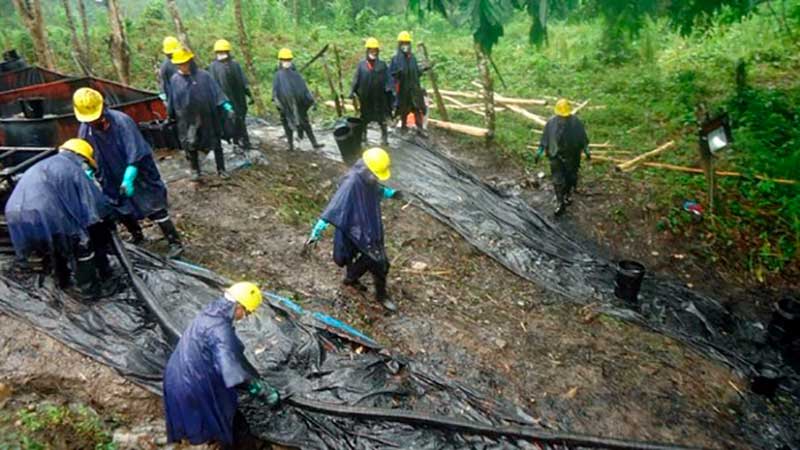

Source: rpp.pe
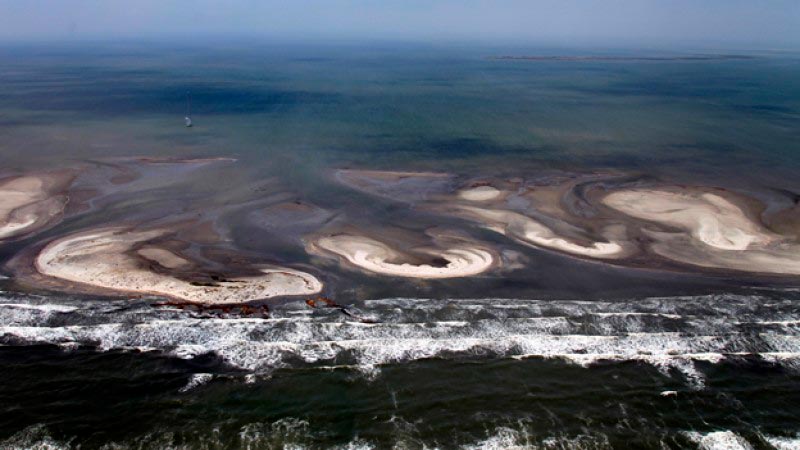

Source: Maruxa Pérez/via mgdsostenible.blogspot.com
Nuclear waste deposited in the soil
Radioactive elements have harmful consequences for soils because the radioactive agents lodge in from the surface to the deepest layers, being able to cause a serious degradation of the soil and even the infertility of it. Radioactivity has important consequences on nearby ecosystems, affecting fauna, flora and the food chain.
Recommended reading: The Anthropocene, the epoch of humans
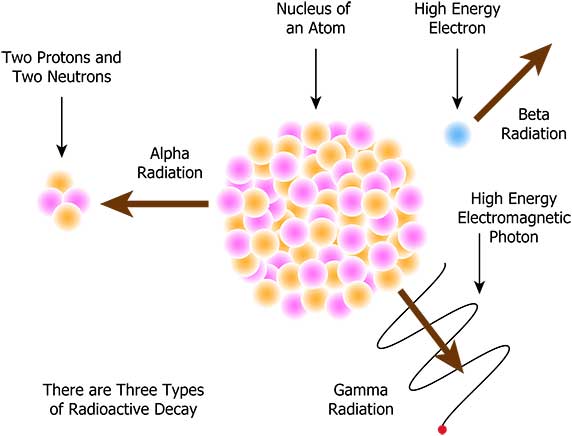
Source: chegg.com
What is a radioisotope?
A radioisotope is an atom of a chemical element that carries out radioactive emissions. “radioisotopes can occur in nature or produce in the laboratory.”
Consequences of radioactivity
Contact with radioactive material increases the risk of cancer and the weakening of the immune system are the main consequences for humans.

Source: Greenpeace

Source: ecoticias.com

Source: Econcientiza

Source: Econcientiza
The fracking and contamination of soils
What is fracking?

Fracking is an unconventional method of extracting oil and gas that requires vertical and horizontal drilling at great depths.
It is a very questioned technology since it delays the use of hydrocarbons of fossil origin and the introduction of more CO2 into the atmosphere, in addition to requiring a large amount of water.
Soil and aquifer pollution by fracking
An aquifer is a volume of water below the surface of the Earth. It is found on all five continents. The total mass of the aquifers is higher than the visible water of lakes and rivers. The vital liquid of the subsoil is an important resource, because it provides a third of the world’s drinking water. This explains the concern of environmental groups for the risk of their contamination in the deep perforations of fracking.

Source: quefuerteeslaciencia.com
Chemicals used in fracking

The Spanish media Eldiario.es reported on 05/30/2015 that “The Agency for Chemical Substances of the European Union has recognized that it lacks control over the products used for hydraulic fracturing” or about its dangerousness. Many of these substances remain in the soil and can contaminate the aquifers and endanger populations that supply water from them.
Fracking and diseases
A study conducted in Colorado, United States, published in the journal Endocrinology, suggested that fracking operations use substances that can result in alterations of the hormonal balance related to infertility and cancer, due to contamination of the surface water of aquifers.
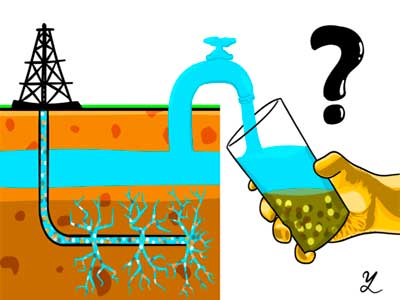
Urbanization avoid the floors
Large cities, as consequences of overpopulation and its high construction density, seal much of the soil on which they are based. This coverage, usually made of cement or asphalt, implies the disappearance of the soil. So the new surface becomes minimal for the development of the vegetation, as well as the retention of water and nutrients. In conclusion, the city replaces the soil, eliminates most of the trees and their function of water absorption, the emission of water vapor, the formation of clouds and rainfall. When this cycle breaks, there is water shortage, drought and finally desertification.
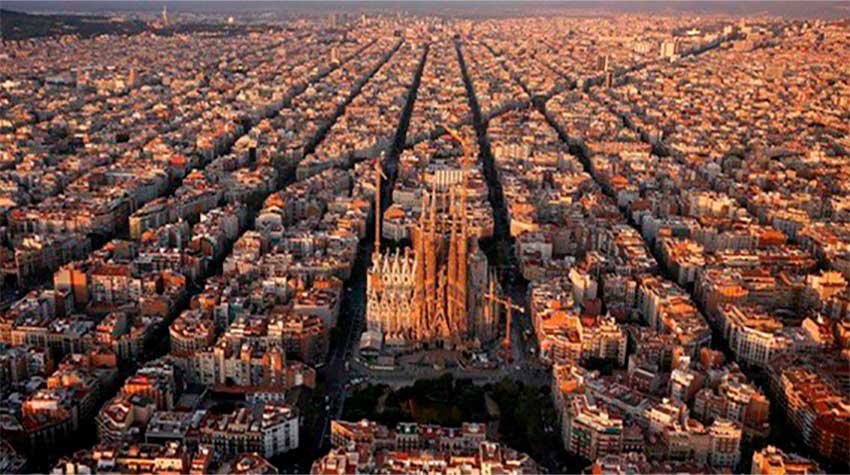

The felling of forests, a multi-faced enemy
The Amazon rainforest is a clear example of the dangers of deforestation and the change of land use. There are presented together the felling of trees to satisfy the timber markets, soybean and oil palm plantations extensively, livestock, oil exploitation, the laying of pipelines and gas pipelines, the construction of roads, hydroelectric dams and urbanization. All these activities steal spaces from the Amazon and its ecosystems, leaving huge gaps in the world’s greatest biodiversity, extinction of species and incalculable consequences. Soils become impoverished, create drought and finally die, becoming in deserts.
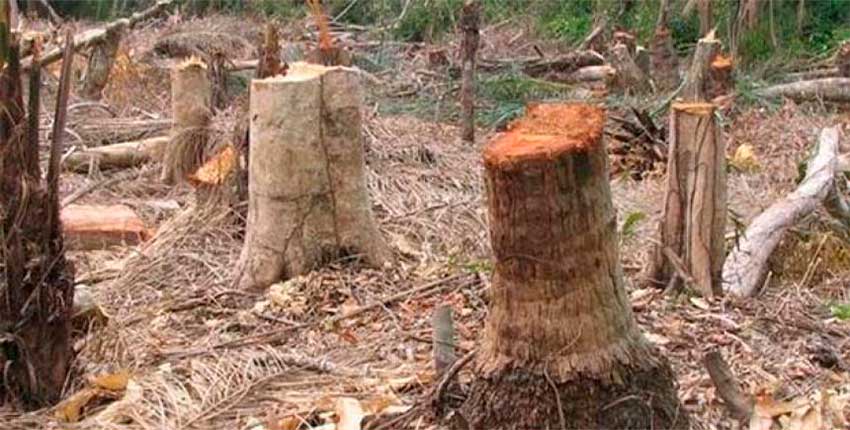

Source: El Heraldo
The monoculture
Monoculture is an agricultural practice characterized by plantations of a single species in large areas. The monoculture uses the same methods of cultivation for the whole plantation, including the prevention of pests. The system is based on large-scale production and the cheapening of agricultural products. Among the most frequent plants planted through monoculture are soy, oil palm, sugar cane, cotton and corn.
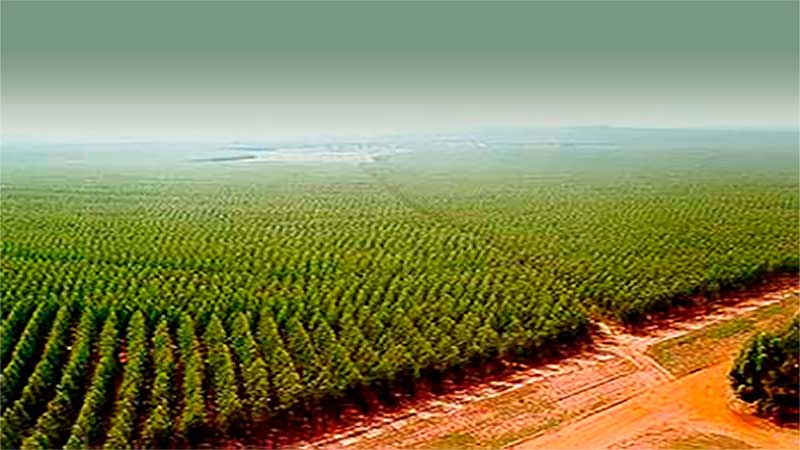

The end of the small family farm
Between the end of the s. XIX and early XX, large plantations of a single species represented the end of the family farm and the diversification of plantings. Unable to compete with these great actors, the small farmers migrated by waves to the cities.
However, to the efficiency and low prices of monoculture, the impoverishment of the soil is contrasted due to the overexploitation of the land. Therefore, the depletion of one or more of its nutrients leads to soil infertility.

Source: es.wahooart.com
Livestock, deforestation and climate change
According to FAO, population growth, wealth growth and urbanization are translating into increased demand for livestock products, particularly in developing countries. World demand is projected to increase by 70% to feed a population estimated to reach 9.6 billion people by 2050. The livestock sector is the world’s largest consumer of agricultural land, through grazing and the use of fodder crops. Due to this, it has a significant negative effect on climate change, soils, water and biodiversity. The natural resources that sustain agriculture, such as land and water, are increasingly scarce and increasingly threatened by degradation and climate change.
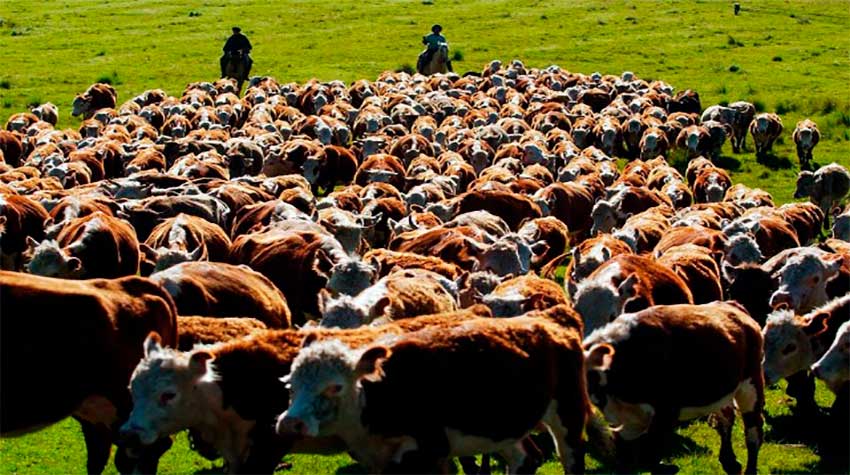

Source: Sembrando Noticias
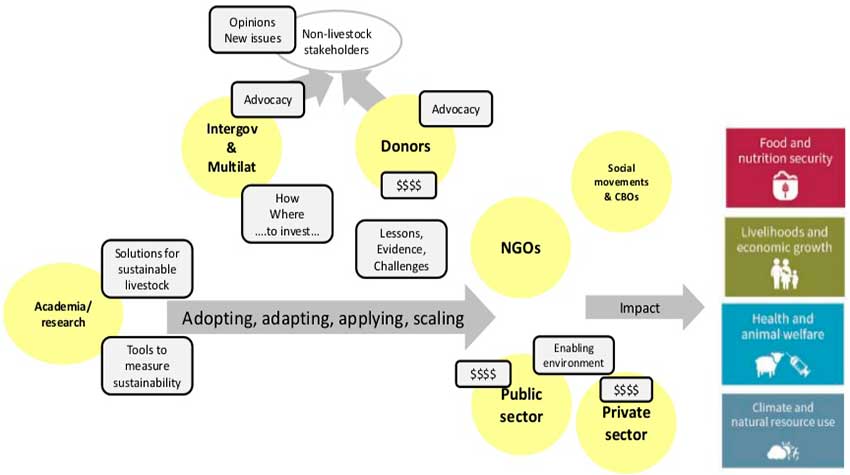
Source: FAO – slideshare.net
The global agenda for sustainable livestock
This FAO agenda aims to catalyze multi-stakeholder action to improve the use of the sector’s natural resources, ensuring their contribution to food security and livelihoods.
Mining and the serious deterioration of the environment
During the open-pit mining process there is such an important impact on the environment that it could be classified as catastrophic damage or massive deterioration. During the construction, excavation and earth movement of this class of mines, huge volumes of abiotic and biotic material are removed from the substrate downwards. In these mega engineering works rivers are altered by drainage, wetlands, coasts and beaches are eliminated and lakes and lagoons are created. During the dredging and extraction of metals or minerals, ecosystems are destroyed, and waste and debris are deposited in nearby areas, thus increasing the area of environmental damage.
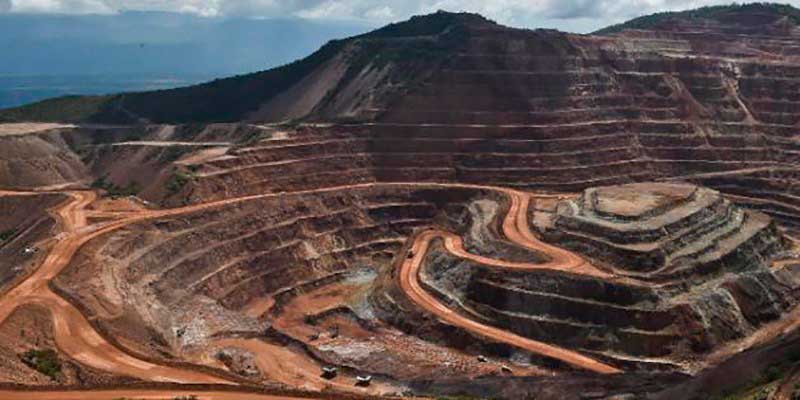

A general view of the Los Filos gold mine in Guerrero State, Mexico, on October 21, 2014. AFP Photo/Ronaldo Schemidt.
Source: Minería en Línea
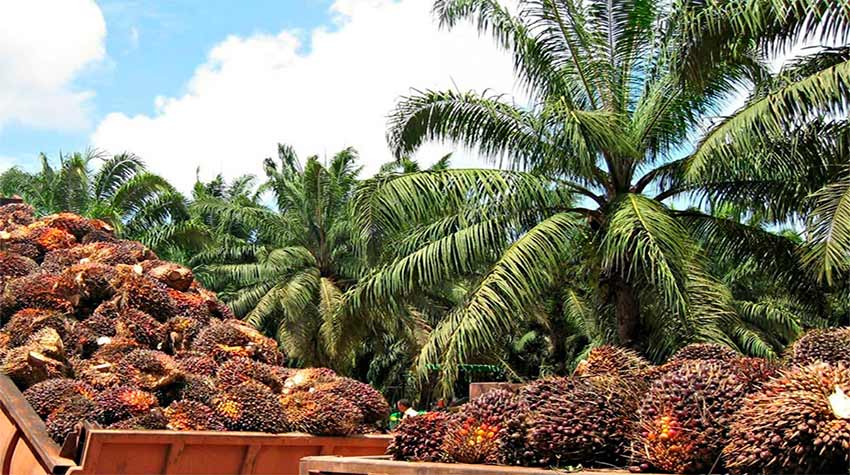
Oil palm and soy, two enemies of soil
The oil palm and its devastating consequences
The oil palm is a plant that in a single hectare can produce about 6,000 liters of crude palm oil, several times higher than that obtained with soybean oil or corn oil, which makes it very profitable.
The expansion of the cultivation of African oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) is generating enormous environmental impacts worldwide. Scientists warn that this type of crops generates devastating consequences on soils transforming large hectares of land into infertile and in some cases irrecoverable.

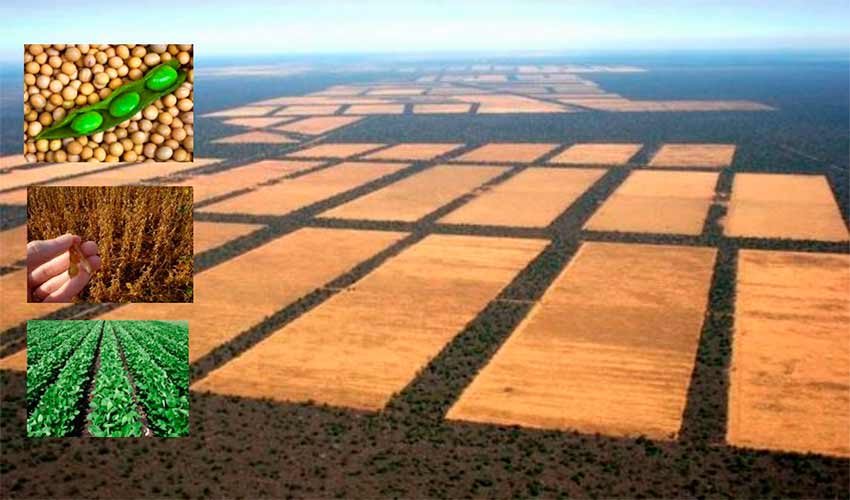
The Soy and its adverse effects on soils
Soy is mainly used to make oil, milk and soy flour. It has a high protein content. Soy is a great substitute for beef and cow’s milk, which represents a food solution for millions of people.
Soy, a monoculture produces negative effects on the soil, such as depletion of the soil and an increasing loss of its fertility. Soy leaves few vegetables remains and therefore its contribution of organic matter is minimal. The use of heavy machinery produces the compaction of soils and consequently erosion ensues.

Source: Paraguay.com
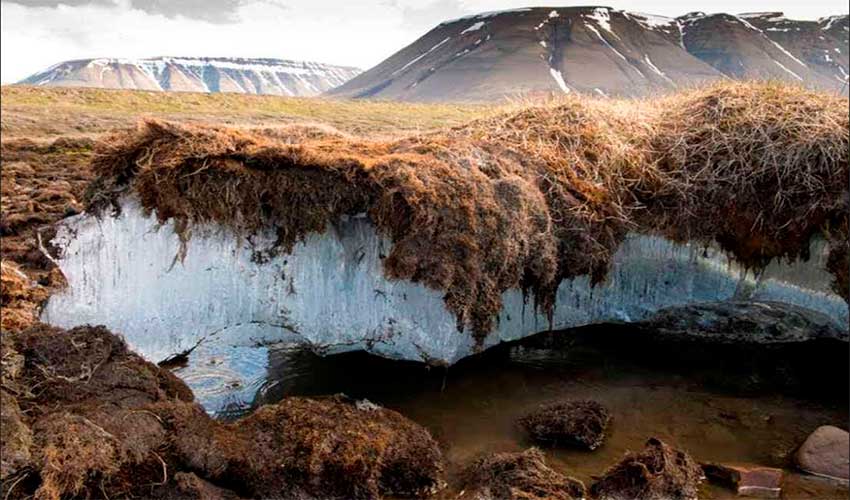
Two latent dangers
What is a permafrost soil?
Permafrost is a frozen ground but without ice. These frozen deserts are extremely rich in organic carbon, accumulated in the subsoil for thousands of years. The tundra is a permafrost soil that remains frozen all year. In the taiga, the soil can freeze during the winter, but the summer months are warm enough for the surface to thaw, although the deeper parts remain frozen. With increasing global warming there is a risk that carbon will be released into the atmosphere, increasing the greenhouse effect and global warming in an chaotic way.

Source: youtube.com
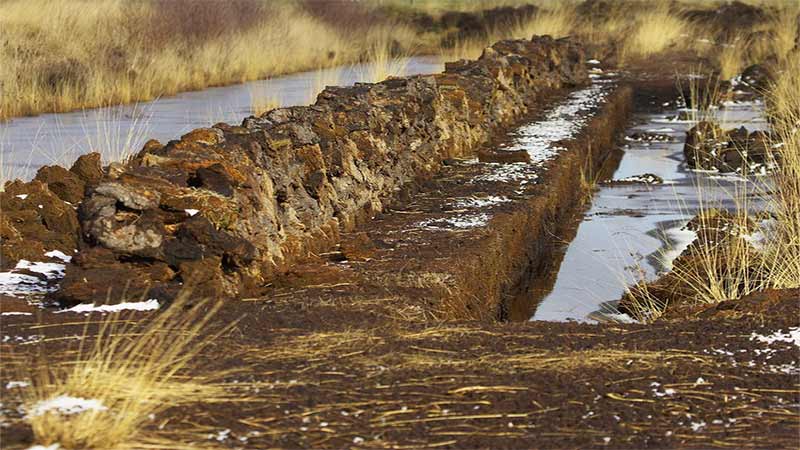
What are peatland soils?
A peat bog is a type of acid wetland in which organic matter has accumulated in the form of peat. The peat bogs are lacustrine basins, generally of glacial origin, full of decomposed or semi-decomposed plant material, known as freshwater peat. Large deposits of carbon are stored in the world’s peat bogs.
In Borneo, the third largest island in the world, shared by Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei, palm oil producers dug huge ditches to drain water and plant their palms. This allowed the release of powerful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Dry peat is highly flammable. In 2006, Indonesia experienced one of the worst fire seasons.

Soil infographics


