Source: Indianapublicmedia.org
Magazine all about Global Warming
Natural global warming, key factor of
life on Earth
The natural global warming of Earth is caused by a phenomenon called greenhouse effect, a particular feature of the atmosphere that makes our planet a very special place and different from the others known so far. This feature has allowed the multiplication of the life of thousands of species that have acquired the most diverse shapes, sizes, colors and movements of translation.

Source: Codigoqro

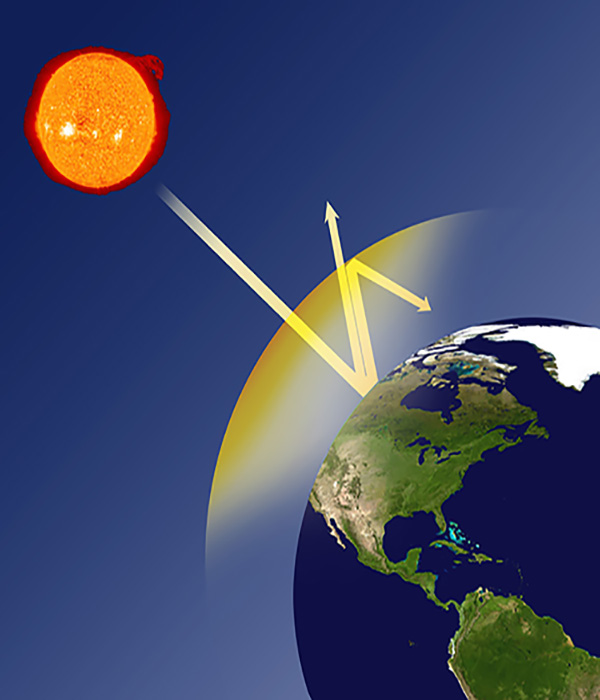
How does work the natural global warming of Earth ?
The greenhouse effect
When the sun’s rays come from space, they bounce off the earth’s surface and try to escape back into the cosmos. In our planet a part is retained in the atmospheric layers and as a consequence the phenomenon of natural global warming takes place, which is manifested by temperatures in a fairly uniform range.Without the greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and others, the average temperature of the planet would be close to an average of 18 ° C below zero. It would be an icy planet, probably uninhabited like most of the others in the Solar System, or at least not fit for life as we know it.This property, together with others, has allowed the multiplication of an enormous biodiversity on Earth.
Source: memosy61.wixsite.com
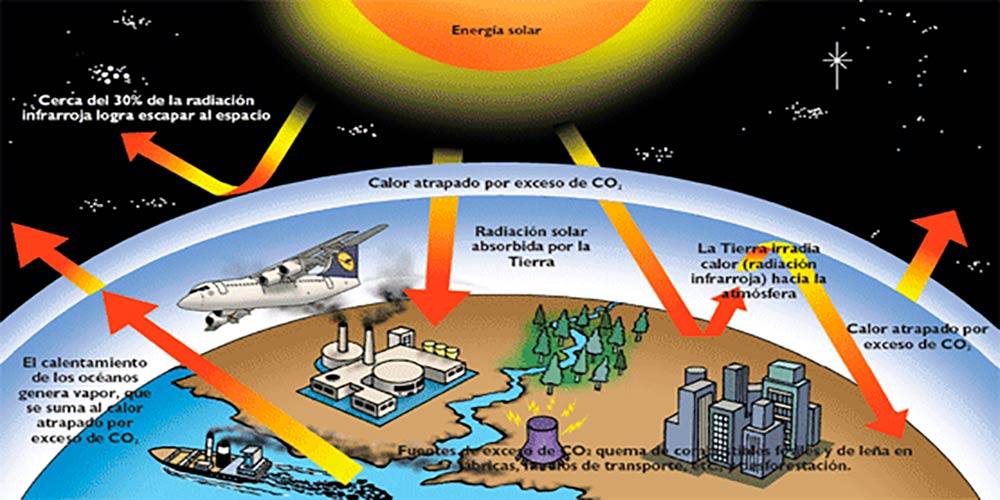
The Anthropogenic global warming
Source: Blog Irma Robles
When we talk about global warming, climate change or greenhouse effect, we refer to current phenomena, of anthropogenic cause, that is, changes related to human activities. These interventions increased the concentration of CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere since the beginning of the industrial revolution in 1750, increasing global warming and, as a consequence, causing important changes in the planet, which we have called climate change.

Source: Felesteen.ps
From the beginnings of machinism, and especially since 1950, an increase in global temperature began, in a slow process from the perspective of human chronometry, but almost instantaneous in the scale of geological times. The slightest increase in temperature has immediate effects on the climate of the planet. That is why the greenhouse effect, global warming and climate change are so linked that it is impossible to talk about any of them without mentioning the other two.

Source: Oaxaca Digital
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, concluded in 2013 that it is extremely probable that human influence has been the dominant cause of global warming observed since the mid-twentieth century. “The greatest human influence has been the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen oxide. These conclusions have been endorsed by the national science academies of the main industrialized countries, and are not questioned by any scientific organization of national or international prestige. ” Wikipedia.
Fourier saw it clear two centuries ago
Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830), a French mathematician and physicist, calculated in 1824 that an object the size of the Earth and with a similar distance from the sun, should be much colder than it really is. He affirmed that our planet was maintained with a temperate climate because our atmosphere retains the heat as if it were under glass. Thus, Fourier has the honor of being the first to use the greenhouse analogy.

Composition: SGK-PLANET
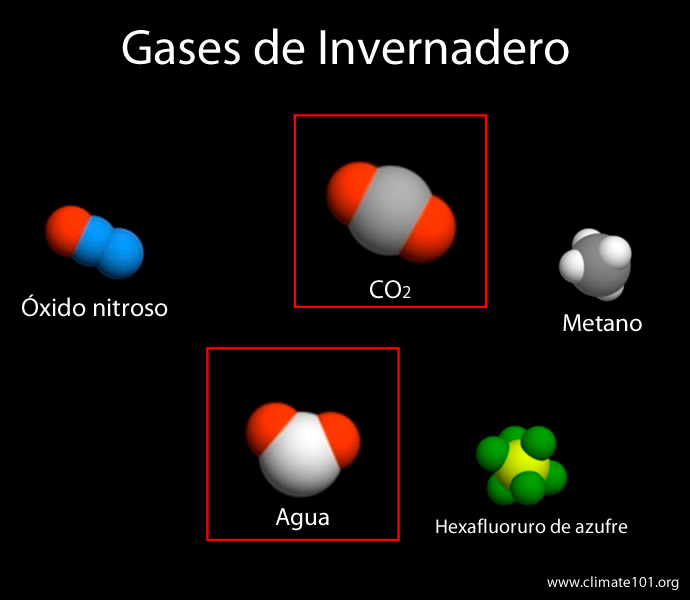
CO2 or carbon dioxide, the gas that contributes the most to modifying the greenhouse effect
Main greenhouse gases
Source: Climate101.org
Greenhouse effect
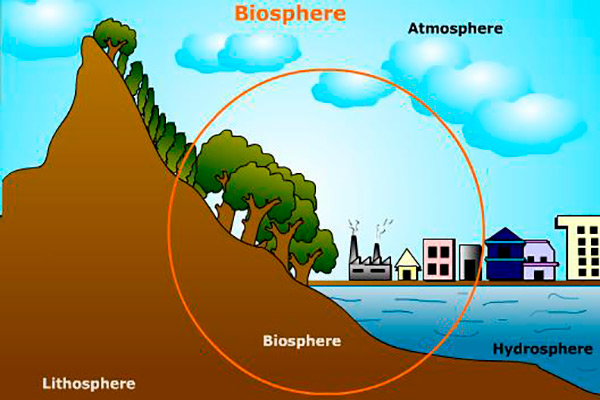
The biosphere, that thin sphere that contains all the life of our planet
The biosphere is a fragile system, susceptible to small physical, chemical and electrical changes. An increase of two, three or four degrees Celsius can cause serious damage to the spice community that we inhabit.
Fuente: Pinterest
The biosphere includes the habitats and transit zones of all living beings on Earth. So it includes the air, sea and land spaces where some species lives or transits on the planet. If we consider 10 km of height in the air and 10 km in the ocean depths, the biosphere has an average thickness of about 20 km. So compared to the dimensions of the Earth the biosphere is a very thin, fragile and vulnerable ring where we live together everybody.
Causes of global warming

Source: AEROSOL la revista

Source: Climate Action Programme

Source: Nautical News Today

Source: Imágenes y fondos

Source: J. Leblanc

Source: InsureForAll
Air pollution using fossil fuels is modifying the greenhouse effect and natural global warming. In this way, what until now has been beneficial for life on Earth can have an opposite effect and cause the extinction of many species.
The 10 biggest CO2 emitters
China 28.21%, USA 15.99%, India 6.24%
Russia 4.53%, Japan 3.67%,
Germany 2.23%, South Korea 1.75%,
Iran 1.72%, Canada 1.71%
Saudi Arabia 1.56%

Have we reached the Anthropocene?

Source: Magnet.xataka.com
The Anthropocene, according to a group of researchers, begins with the discovery of radioactive waste left by atomic bombs. “We have already changed the Earth: the Anthropocene is the moment in which humans manage to change the life cycle of the planet, when humans remove the planet from its natural variability,” explains Alejandro Cearreta, a Spanish scientist and member of a
group of 35 specialists, who after seven years of research agreed to consider the Anthropocene as a new geological epoch within the Quaternary period.
Increase in global temperature in numbers
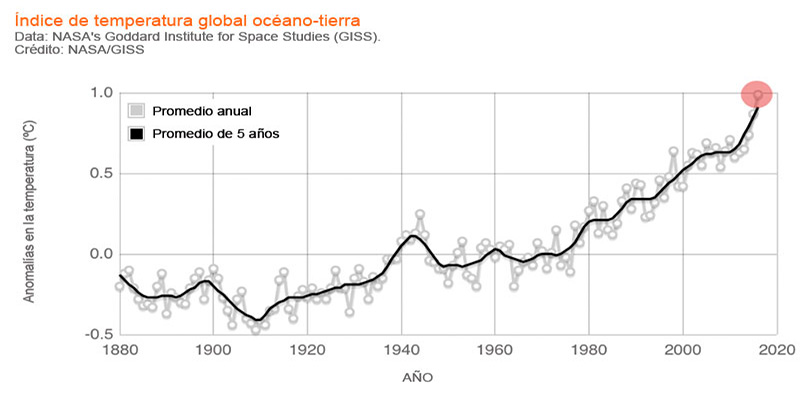
Source: NASA/GISS
Unimaginable temperature
40ºC in summer of 2018 in Siberia
Yes, you read well, they are not -40 they are +40
“The main effects were the melting of sea ice in the Laptev Sea and the permafrost [the permanently frozen soil or underwater layers] of the land and underwater surface.” From: Diario El País, Spain

Rarely we talk about permafrost, but it is much damage that may result
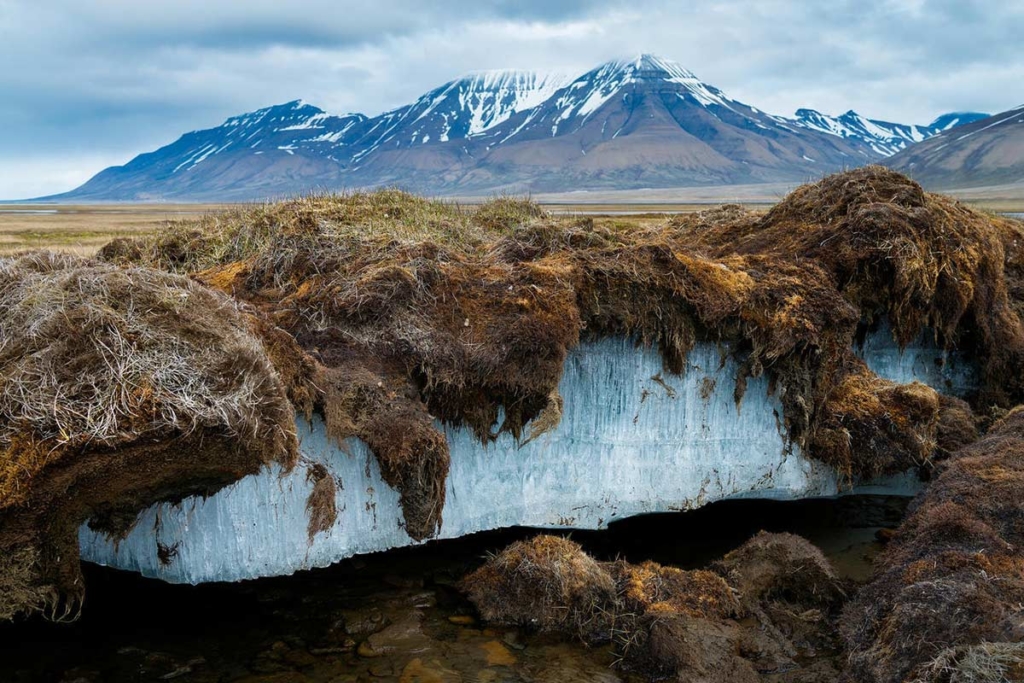

Source: Fecupral.sk
What is permafrost? It is frozen ground, but without ice, that we could imagine as a desert of frozen earth. Permafrost soils are extremely rich in organic carbon, which has accumulated in the subsoil for thousands of years. The tundra is a permafrost soil that remains frozen all year. In the taiga, the soil can freeze during the winter, but the summer months are warm enough for the surface to thaw, although the deeper parts remain frozen. With increasing global warming there is a risk that carbon will be released into the atmosphere, increasing the greenhouse effect and consequently global warming itself.
Permafrost – what is it?
Permafrost layer in an Arctic region
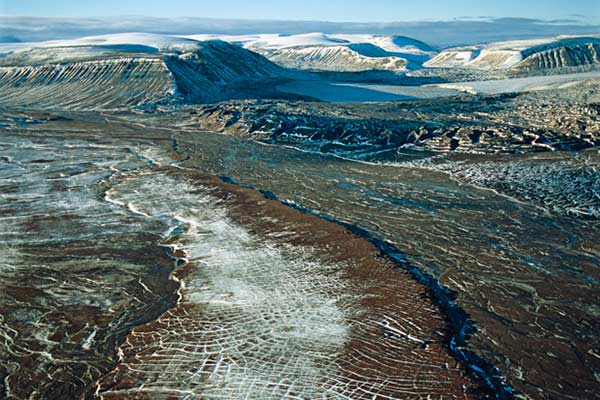

Source: Mario Picazo – Eltiempo.es
Permafrost in the world
Mostly it is distributed in areas near the poles. In the northern hemisphere mainly in Alaska, Canada, Siberia, Norway and Tibet. In the southern hemisphere it is found in the Georgias and Sandwich Islands. All this amounts to about 25% of the total Earth’s soils. In the case of Russia, it should be noted that more than 63% of the territory sits on permafrost zones and therefore there are towns and cities built on these unstable soils.
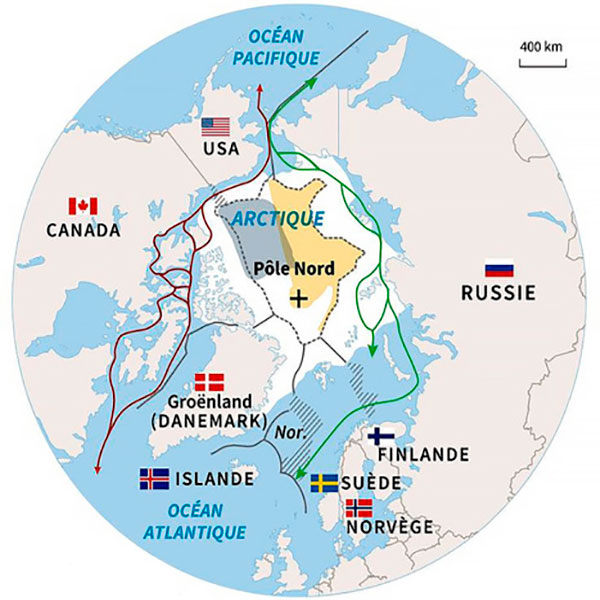
Source: Scoop.it
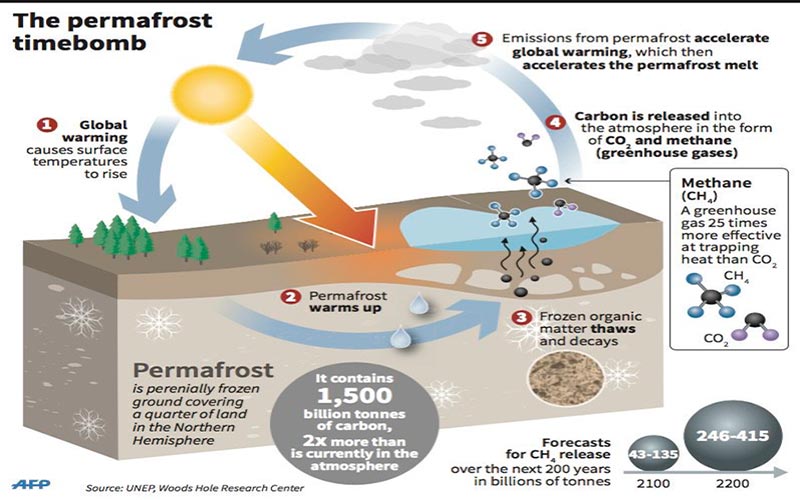
What are the threats of permafrost?
According to one estimate, permafrost soils contain about 1700 million tons of carbon, almost double the total amount of carbon currently in the atmosphere. When the soil remains frozen, the carbon is inert, but when the permafrost is thawed by increasing the temperature, the decomposition of the organic matter increases through the microbial activity. In that case amounts of CO2 and methane would go into the atmosphere. In Alaska, since the 1970s is happening, they are escaping from their CO2 emitting soils.
Finally, the concentration of methane in the atmosphere is 220 times less than CO2, but 23 times more potent. The infographic of Tibet indicates that methane is by long the highest volume gas in the subsoil.
What Are Tundras?
Permafrost in Alaska
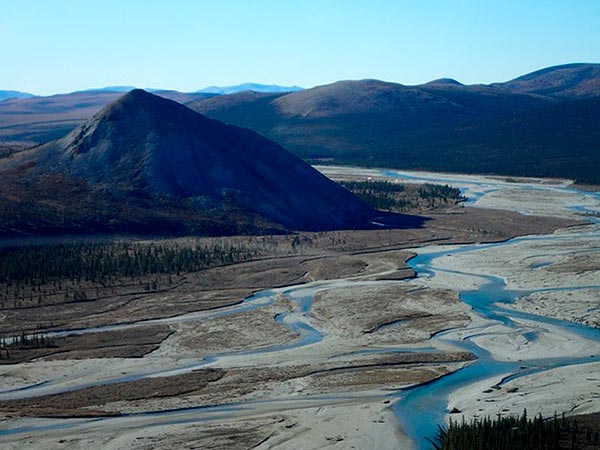

The Agashashok watershed in Noatak National Preserve, Alaska / NPS Photo / Ken Hill
The “Vault of the end of the world”
It is the largest seed warehouse in the world, created to safeguard the biodiversity of the crop species that serve as food in the event of a global catastrophe. It is a huge underground pantry located on the island of Spitsbergen, Norway, 1,300 kms north of the Arctic Circle.

Source: LaVanguardia.com
The huge vault was created to withstand earthquakes, impacts of nuclear bombs and other disasters. It is shielded against volcanic activity, radiation and rising sea level, and in case of electrical failure, the permafrost from the outside will act as a coolant. But here is the problem. With the threat of the melting of the permafrost the vault would lose the advantage that gives it the place where it was built, that is to say, its refrigerant characteristic, with which the seeds would be lost.
From lavanguardia.com, 05/26/2017: “The World Seed Bank, 1,300 km north of the Arctic Circle, faces water seepage caused by the melting of permafrost. (…) built protect the richness and variety of plants and crops across the planet, faces the worst threats: climate change.”
The forests destruction increases
global warming
Trees produce oxygen, necessary for most living things, and in turn absorb CO2 or carbon dioxide, the gas that contributes the most to global warming. During photosynthesis, the process carried out by trees and most plants, they absorb and store CO2, which is fixed in its roots, trunks and leaves in the form of carbon. Although plants take oxygen from the air and re-enter carbon dioxide, the final balance is favorable to the extraction of CO2 from the atmosphere. This advantage is lost by deforesting the forests.
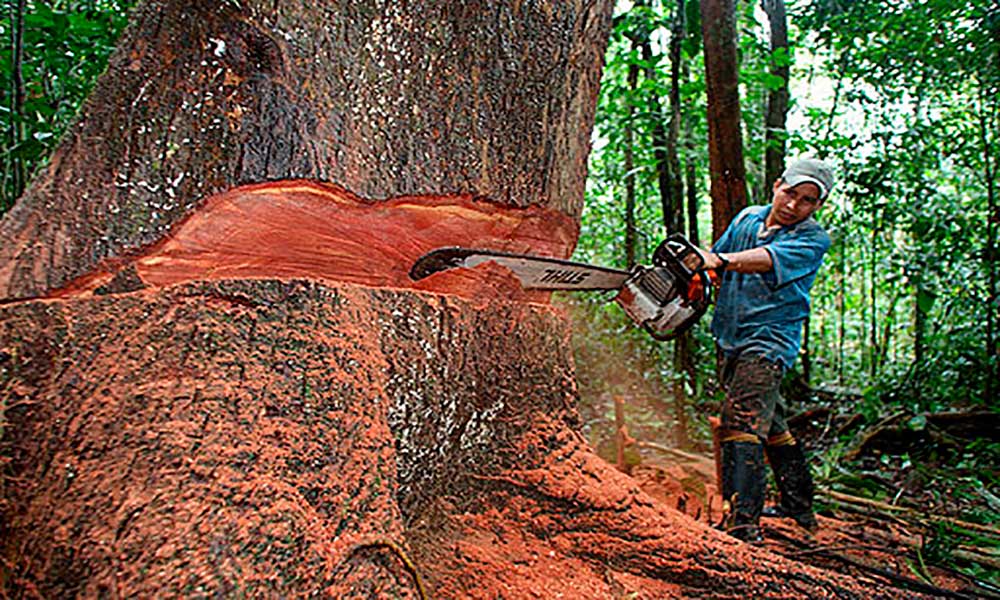

Source: Elnovedades.com
Homo sapiens, the only species that destroys its habitat – It is urgent to decree zero tolerance for the felling and burning of forests
The massive deforestation of forests seems unstoppable
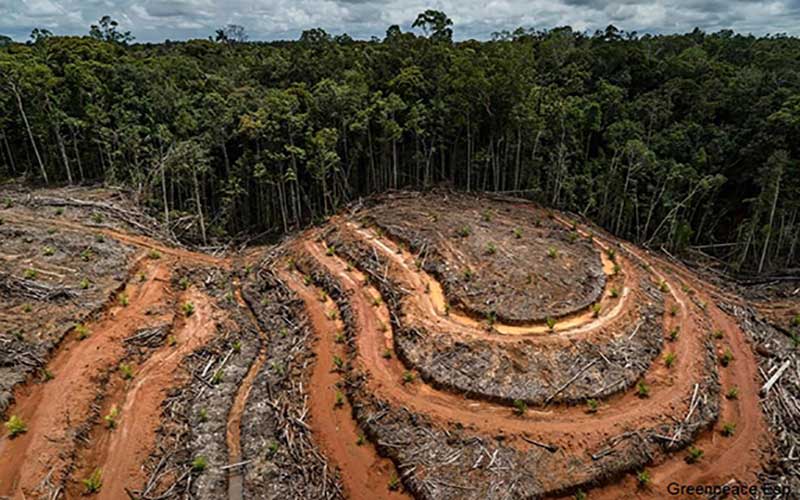

Source: Greenpeace
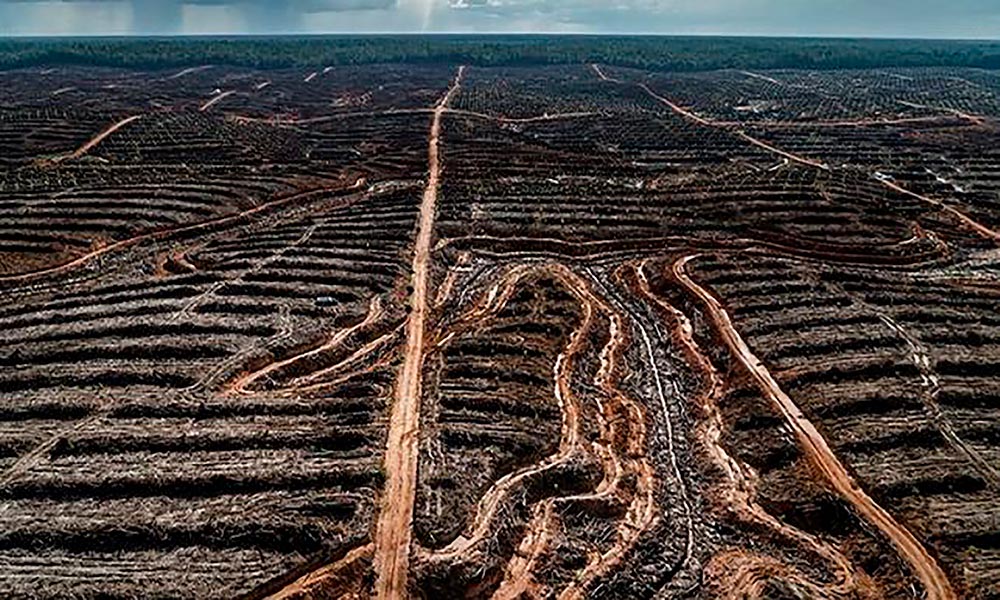
Spiral terraces made to plant palm trees in the place where they cut the trees of the Borneo jungle
The forests destruction increases fires and global warming
The felling of forests has a double negative effect on the climate. In the first place, the felled trees, by not producing oxygen or being able to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, cease to function as lungs of the planet, increasing the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Second, forest fires release CO2 jets into the atmosphere, produce more heat and heat more fires. A vicious circle that increases the problem more than many people think.
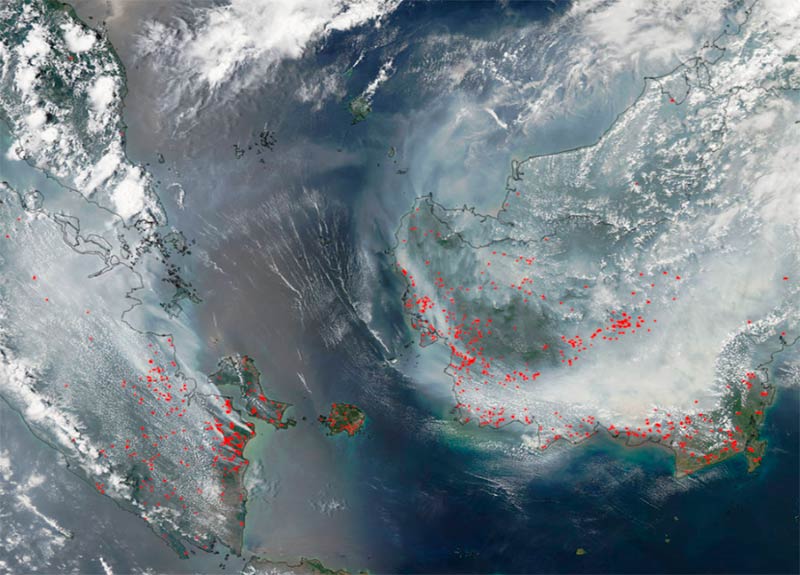

Photo: NASA
Fires and extreme smoke in the Borneo jungle seen from space
Why are there so many forest fires in the forests?
Burning is the most economical method to clear land for planting. After a forest area is deforested, the plant remains are burned. In Borneo the fire was used for the massive sowing of the oil palm, after the hostile felling of trees.
The fire was also used to evict the occupiers from lots of land in the struggle for the possession of sowing areas. These fires are used in a controlled manner, but not infrequently they have gone out of control, especially during droughts, spreading quickly and forcefully, burning large areas of forest. Borneo already had its own climate change. From the rainforest it became an arid and dry place. Some scientists think that these effects may have come to Australia and even to distant Chile, where fires have intensified since the Borneo disaster began.
Burning forests in Borneo

Source: Puranic
Millions of trees go to the world’s mega sawmills
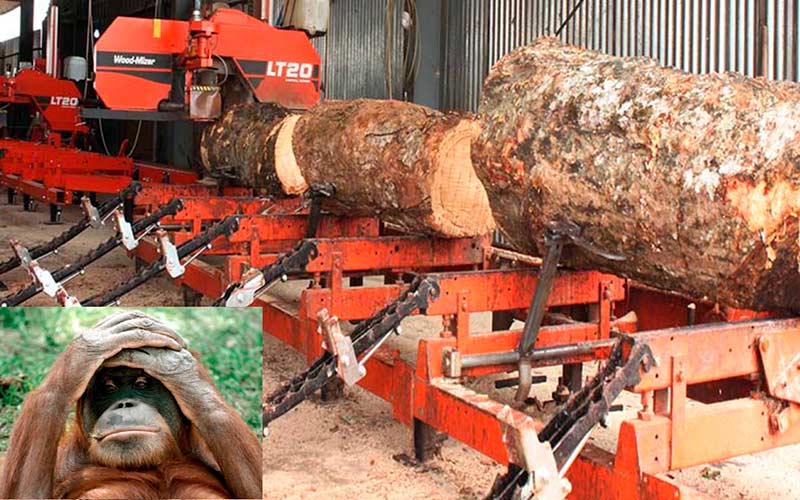

Source: Wood-Mizer Africa – Modif . SGK-PLANET
Deforestation of forests erases contless habitats from the map. In this way, the extinction of species occurs and the consequent breakdown of the food chains, affecting biodiversity.
<iframe width=”370″ height=”208″ src=”https://www.youtube-nocookie.com/embed/Ic-J6hcSKa8″ frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture” allowfullscreen></iframe>

Source: cumcfw.org
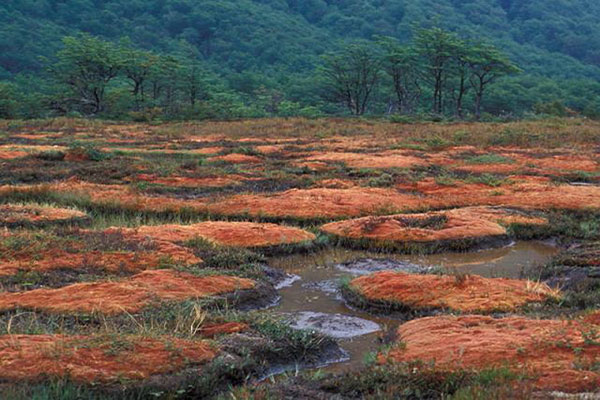
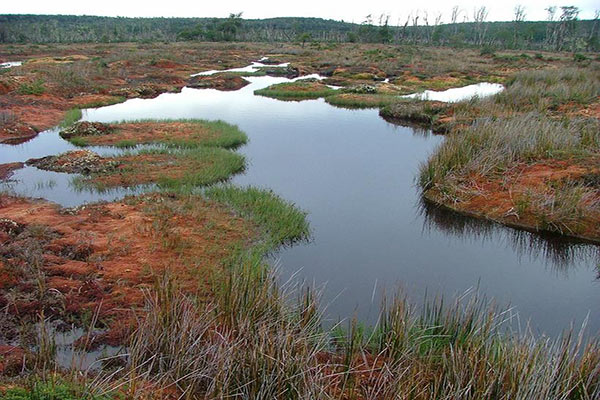
What are peat bogs and how do they affect the greenhouse effect?
“The peat bogs are wetlands with a thick layer of organic soil. Peatlands cover only three percent of the earth’s surface, but store 20 percent of the world’s soil carbon. In many parts, peatlands are drained and used for agriculture and forestry. When drained, peatlands become net sources of greenhouse gas emissions … ”
Forests of peat bogs burned intentionally

Source: Eldiario.es

Source: Bárbara Saavedra

Source: mnhn.cl
Borneo ya tuvo su cambio climático
Borneo already had its climate change
In the south of the island, much of the vegetation grew in the form of peat bogs. These are composed of deep layers of organic matter accumulated over thousands of years.
To plant in peat, the palm producers dug huge ditches to drain the wáter to dry the land.
With this act they released large amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, which contributed to global warming.
The peat when drained quickly decomposes and releases amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Dry peat is highly flammable. (…) In 2006, Indonesia experienced one of the worst seasons of fires that are remembered, when smoke from the fires of Sumatra and Kalimantan triggered a carbon bomb and enveloped the region in a thick haze visible from space. That year the fires carbonized a thousand orangutans.
Consequences of global warming
Thawing of the poles and glaciers

Source: Medium
Droughts, and rivers disappearance

Source: The Guardian
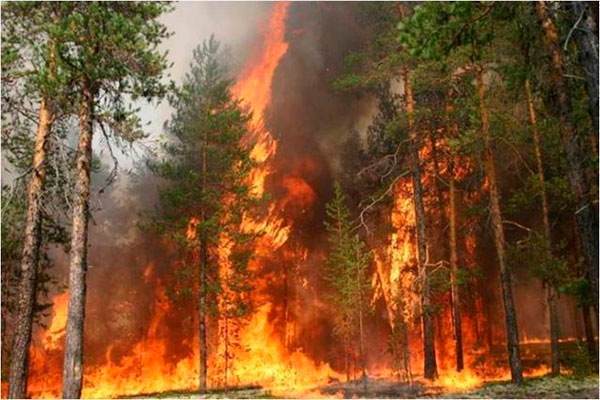
Wild Fires

Source: Kerchak.com
Great floods
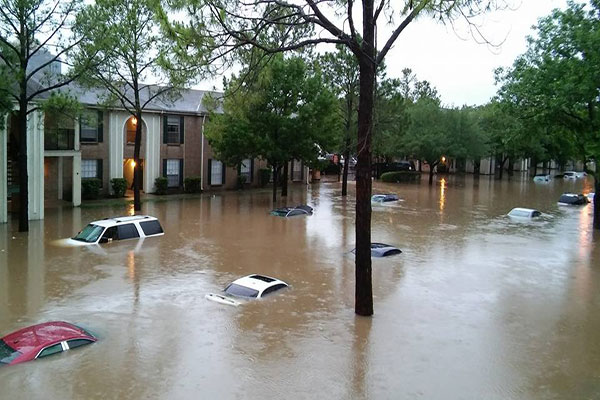

Source: Periodicocontacto.com.mx
Unusual hurricane behavior
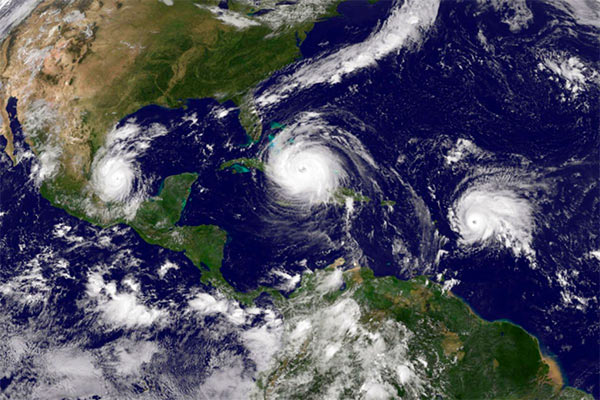

Source: Telemundo
More frequent tornadoes
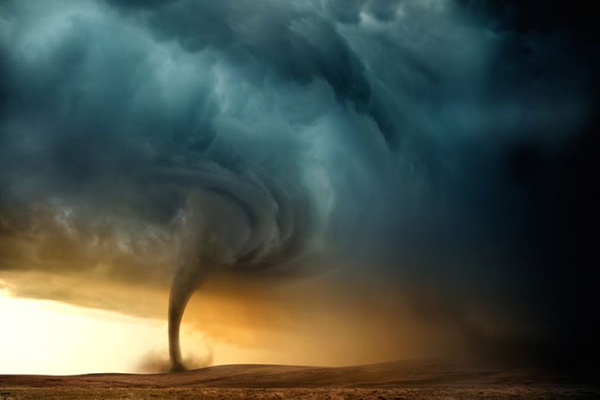

Source: Bles.com
Imbalance of biodiversity
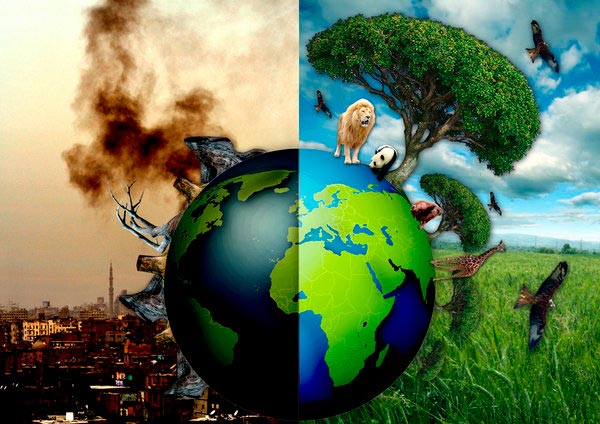

Source: Slideshare
Famine due to prolonged droughts

Source: Catedragrobank.udl.cat
* For more details on the consequences of global warming, see the All about Climate Change Magazine
Global warming over time
Past
Source: Pinterest
With the Industrial Revolution, emissions of greenhouse gases and an increase in global temperature began significantly. The use of coal in steel mills and factories, and the commissioning of railways and steamboats initiated the increase in global warming. Then automotive vehicles and other transport systems moved with gasoline, gas and diesel were added.
Present

Source: Hoy Los Ángeles
Since 1950, the incorporation of millions of internal combustion vehicles began. Added to the rapid deforestation of forests and the increase of livestock and agriculture. Global warming start to be seen as a serious problem. The first world climate conference was held in Stockholm in 1972. The Paris Agreement was presented in 2015 and will enter into force in 2020. Already 197 countries have signed the document.
Future

Source: Marvel Wiki
The future has never been easy to predict, and even less in the face of the vertiginous changes that are expected, such as artificial intelligence, new materials, electric cars, solar energy, wind energy and green cities. If with these technologies we can substitute fossil fuels for clean energies, the fight against global warming will have won an important battle and life on the planet will be safe.
The fight against global warming
Accepted by almost all countries

Goal: two degrees centigrade less

* More information on these topics in the Paris Agreement Magazine
Sustainable development

Source: Ucc.edu.co
Sustainable development refers to present needs with the premise of not
compromise the needs of future generations, trying to do so
the balance of the socioeconomic and environmental aspects.
Three keys in the fight against global warming
Source: Yucatanalinstante.com
Mitigation
It is a word that means to attenuate or soften a negative thing, such as an illness or a headache. In the case of global warming, mitigation refers to the reduction of GHG emissions. They also include the improvement of the sumps to increase the absorption capacity of said gases. Also considered are programs such as carbon or energy taxes, and incentives for voluntary GHG reduction and its replacement by clean energy.

Source: Cronista.com
Adaptation
It refers to the actions that must be carried out to prevent changes that can produce undesired effects. In the case of global warming, adaptation includes initiatives and measures to reduce the vulnerability of natural and human systems to climate change. Countries and communities must implement preventive measures and practices to avoid probable harm. Short and long-term measures must be contemplated, through environmental management, planning and disaster management.

Source: Eldiario.es
Resilience
Resilience is the ability of a species or system to recover from a disturbing agent. In terms of global warming, resilience refers to the capacity of an ecosystem to absorb disturbances without significantly altering its structural and functional characteristics, and can return to its original state after the adverse factor has ceased. The Paris Agreement places special emphasis on increasing mitigation, adaptation and resilience capacity to reduce vulnerability to climate change.
The Green Climate Fund

Source: Geoglobal803.weebly.com
It has been established
to help the
developing countries
to meet
goals
in the
Fight against
climate change

