FAQs about Permafrost

5. Is Siberian permafrost thawing faster?
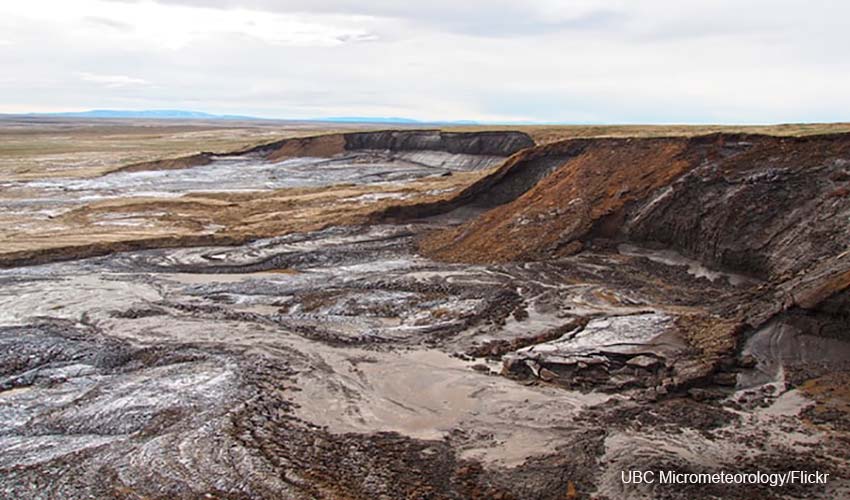
Forest fires have increased during 2020 in Siberia in an environment of record temperatures. As a consequence, permafrost is thawing at a higher rate than estimated and sea ice is melting alarmingly.
According to the Washington Post, “In Siberia and much of the Arctic, profound changes are taking place faster than scientists anticipated just a few years ago. Changes that previously seemed decades away are now happening, with potentially global implications.”
Vladimir Romanovsky, a researcher at the University of Alaska at Fairbanks, said: “The pace, severity and extent of the changes are surprising even too many researchers who study the region for a living. Predictions for how quickly the Arctic would warm that once seemed extreme “underestimate what is going on in reality. The temperatures occurring in the High Arctic during the past 15 years were not predicted to occur for 70 more years.”
“Neither Dallas nor Houston has reached 100 degrees this year, but in one of the coldest regions in the world, Siberia’s” Cold Pole “, mercury rose to 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius) on June 20 (2020).
If confirmed, the record in the remote Siberian city of Verkhoyansk, about 3,000 miles east of Moscow, would become the highest temperature in the Arctic since record keeping began in 1885.”
FAQS about Permafrost
1. What is permafrost and where is it located?
2. Are there frozen soils without ice?
3. What is the function of permafrost?
4. What dangers does permafrost pose?
5. Is Siberian permafrost thawing faster?
6. Is Russia the most vulnerable country due to permafrost?
7. What are the bacteria related to permafrost?
8. Can bacteria hibernating for millions of years in permafrost be activated?
9. Is there permafrost in the southern hemisphere?
10. What is the difference between the tundra and the taiga?
Other secctions of Permafrost
Article
Magazine
You can also see it in…
Infographics
Photo Gallery.

Video Gallery

