The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reported that 2024 was the warmest year on record. Current projections predict that 2025 will be even warmer.
Among the consequences of the unstoppable rise in temperature are extreme heat and cold waves, devastating floods, massive forest fires, droughts, hurricanes, tornadoes, and other catastrophic events.
What are we owing to these events?
What has so far been an advantage is now becoming a threat.
The greenhouse effect occurs in the troposphere, the lowest layer of the Earth’s atmosphere, and retains some of the heat produced by the sun’s rays. This protects Earth from becoming a frozen planet, crucial for life, unlike the other planets in the solar system, which remain frozen and devoid of life.
Beginning with the Industrial Revolution (1850s), carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions into the atmosphere began to increase, exacerbating the Earth’s natural greenhouse effect. As a result, global temperatures started to rise, accelerating unstoppably from the 1950s until now, a phenomenon known as global warming.
In the following graph from the Met Office (the United Kingdom’s National Meteorological Office, founded in 1854), we can observe the evolution of global temperatures and the projections for 2025.
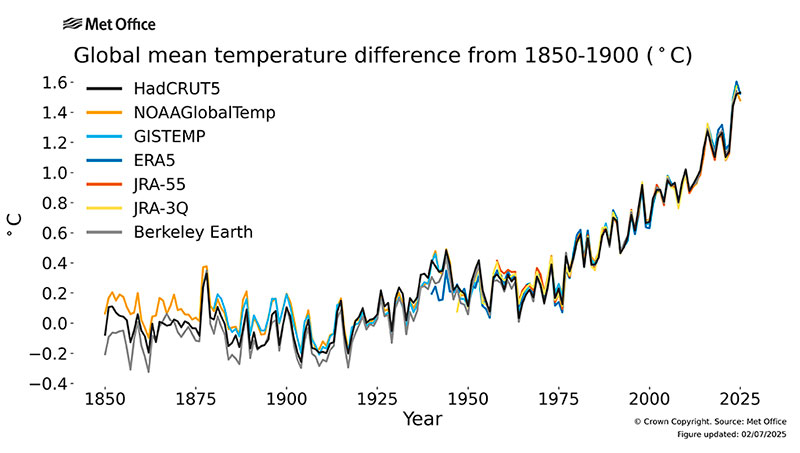
Figure. Projection of average monthly temperatures to 2025. Translation by Aixa Chacin.
Source: Met Office. Data by HadCRUT.4.6.0.0., NOAA Global Temp v5 and GISTEMP v4. Met Office.gov.uk
Credits: United Kingdom Meteorological Organization (WMO) and Met Office, meteorological service of the United Kingdom. Data ©Crown Copyright. Met Office and WMO.
License: Images and CSV data from the Met Office Climate Dashboard under Licence: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ Met Office image available from https://climate.metoffice.cloud/temperature.html#content
As global warming has intensified, the adverse effects on the climate have also increased, a phenomenon known as climate change. This initially had little noticeable impact and went unnoticed by most people. However, over time, the temperature curve has become steeper, multiplying the consequences of global warming, such as heat and cold waves, droughts, massive floods, melting glaciers, fires, and hurricanes.
Heat and cold waves
A heat wave is a sequence of abnormally high temperatures relative to a region’s historical average that can last for several days. As of this writing, Europe is experiencing a severe heat wave. In Spain, some regions have reached 46°C. In Germany, temperatures reach 40°C by July 31. A recent NASA report warns that certain regions of South America could face extreme heat conditions, making them uninhabitable for humans.
Meanwhile, the United States, Canada, and Mexico experienced extremely low temperatures in the first months of 2025. In June and July, Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay suffered a polar cold wave with record low temperatures and several deaths.
Droughts
Drought is defined as a temporary shortage of water in a location, resulting in insufficient water to meet the needs of humans, plants, and animals that inhabit the area. Today, much of the planet suffers from water shortages. In Mexico, four states are currently experiencing severe drought: Chihuahua, Mexico City, Guanajuato, and Querétaro.
Climate change has been evident in 2025, through recent catastrophic events:
California, United States. The megafires of January 7 to February 1, 2025.
Texas, United States. The catastrophic floods in July 2025.
Valencia, Spain. The DANA phenomenon in October 2024.
A DANA, or Isolated Upper-Level Depression, is a meteorological phenomenon characterized by an isolated mass of cold air in the upper atmosphere, which at a given moment separates from the general atmospheric circulation. These depressions can generate intense rainfall, storms, and, in some cases, extreme weather conditions such as the catastrophic floods in Valencia.
Future events that are on the horizon:
“As the planet warms, rainfall events will become more intense and frequent. Warmer oceans, more intense storms, and a warmer, wetter atmosphere, unleashing torrential downpours”. CNN
Conclusions
The climate crisis, caused by human activities, is making extreme weather more severe and frequent each year. It is urgent to reduce greenhouse gas emissions caused by the burning of fossil fuels. It is urgent to reduce oil and natural gas exploration, extraction, and financing. It is also urgent to reduce exploration, drilling, and financing for the oil sector.
Sandor Alejandro Gerendas-Kiss
SGK-PLANET Editor
Surces
Laura Paddison. Extreme heat is a killer. A recent heat wave shows how much more deadly it’s becoming. CNN Español. (Jul 9, 2025). Retrieve of https://edition.cnn.com/2025/07/09/climate/europe-heat-wave-death-toll-global-warming
Sophie Tanno, Laura Paddison, Benjamin Brown (CNN), Paul Mosquera (CNN Español). Spain hit by deadliest floods in decades. Here’s what we know. CNN (Nov. 1, 2024). Retrieve from https://edition.cnn.com/2024/10/31/europe/spain-deadly-flash-flooding-wwk-intl
United Nations. Climate Actions. Causes and Effects of Climate Change. UN (online) Retrieve from https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/science/causes-effects-climate-change
United Nations. UN Water. Water Facts. Water and Disasters. UN (online) Retrieve from https://www.unwater.org/water-facts/water-and-disasters
Met Office Climate Dashboard. Global Temperature. Retrieve from https://climate.metoffice.cloud/temperature.html#content







Leave A Comment