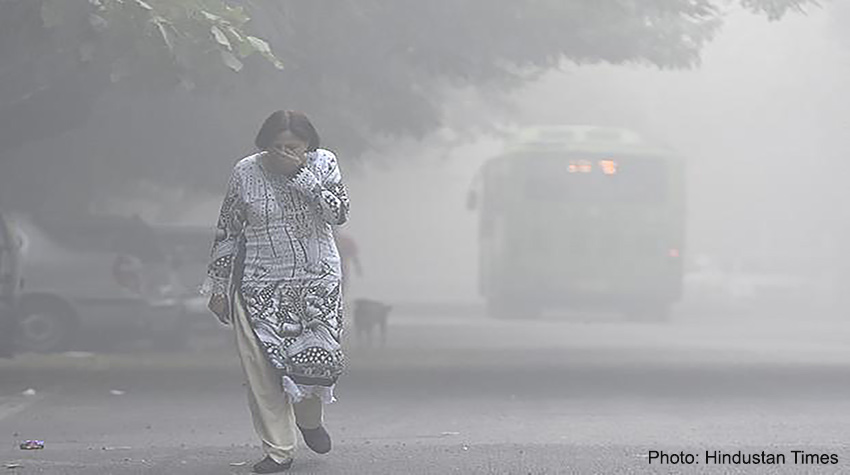
FAQs about Air Pollution

4. What are the main air pollutants?
To the troposphere we send massive emissions of gases and particles. Among these, monoxide and carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and trioxide, nitrous and nitrous oxides, nitrogen dioxide, methane and freon gas. The particles correspond to dust, fumes, mists and aerosols. Powders of industrial origin contain heavy metals such as iron, zinc and lead. Those that come from eroded soils have mineral particles, animal waste and dried vegetables. Fumes and mists are sets of gases that carry various particles with them. The aerosols originate clouds of liquid or solid corpuscles suspended in the atmosphere. Some of these pollutants remain in the air for years and others return to earth through acid rain.
The emissions of carbon dioxide and methane modify the natural greenhouse effect of the Earth, causing progressive increases in the temperature of the planet. Global warming brings climate change consequently. If the objectives and actions contained in the Paris Agreement cannot be achieved, we can expect serious damage to the Earth, as most scientists estimate.