FAQs about Climate Change

2. What are the causes of global warming?
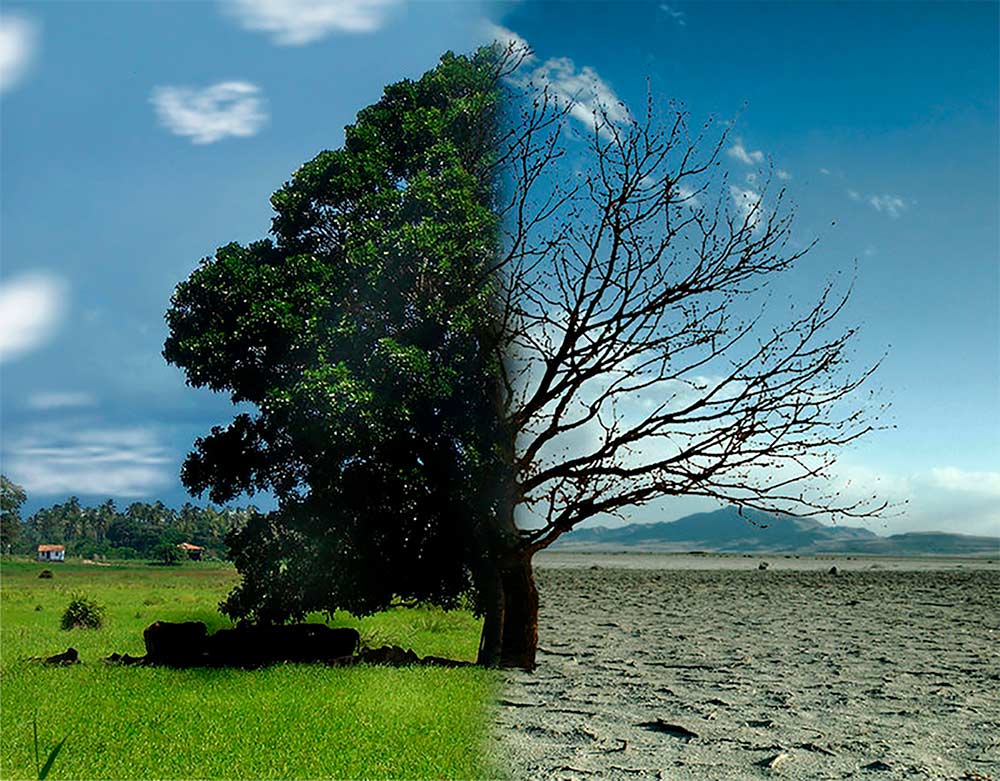
The cause of the natural global warming of the Earth is a phenomenon that has been occurring for millions of years, due to special characteristics of our atmosphere, which we have called the greenhouse effect. Infrared rays, one of the components of the sun’s rays, come from space, bounce off the surface of the planet and try to escape back to the cosmos, but a part is trapped by some gases in the atmosphere, especially carbon dioxide (CO2). As a result, the greenhouse effect occurs, a condition that allows an acceptably uniform temperature, key to life on the planet. If this did not happen, Earth would be an icy planet, probably uninhabited like most others, or at least not fit for life as we know it.
The causes of anthropogenic global warming are due to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, produced by human activity, which adds extra amounts of CO2 and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. GHG emissions intensified since the beginning of the industrial revolution, in 1750, and especially in the 1950s. Since then, the increase in temperature on our planet has been recorded. Most of this increase comes from the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, gas and oil, used in industry and transport. Another part comes from the deforestation of forests and the intensification of the livestock industry.
CO2 is only 0.04% of the total gases in the atmosphere, but with such minimal participation, it is responsible for the greenhouse effect. The concentration of CO2 in recent years broke a record by passing the 400 PPM, parts per million, for the first time since Homo sapiens appeared on Earth.
FAQs about Climate Change
1. What is climate change and what is its origin?
2. What are the causes of global warming?
3. What are the consequences of climate change?
4. Are there examples of recent climate changes on Earth?
5. Why and how much will sea level rise in the future?
6. What are glaciers, icefield and Arctic ice and why are they related to climate change?
7. Is permafrost a climatic weather bomb due to global warming?
8. How will climate change affect humans and other species in the future?
9. What is the role of mitigation, adaptation and resilience to climate change?
10. How can we lose the fight against climate change?
11. What would happen if climate change could not be stopped?
12. Why the Amazon rainforest is the lung of the world?
13. Is the Amazon forest in danger of disappearing?
14. Have we reached the Anthropocene?
Other sections of Climate Change

Pioneers of Climate Change
At all times and in all sciences, there have always been visionaries, those people who anticipate situations long before other persons can glimpse them. This is the case of Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830), a French mathematician and physicist, who in 1824 calculated that an object the size of the Earth and with a similar distance from the sun, it should be much colder to what our planet is really like. He affirmed that it was maintained with a temperate climate because the atmosphere retains the heat as if it were under glass. Thus, Fourier has the honor of being the first to use the greenhouse analogy…

Climate change, what is it and what are its causes?
Anthropogenic climate change is the variation of climate status attributed to human activity that alters the composition of the atmosphere and has consequences on the entire planet. The main cause of climate change is global warming caused by emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG), of anthropogenic origin, among which CO2 is the most frequent. The sources responsible for these emissions are the burning of fossil fuels such as oil, coal and gas, used mainly in industry and transport.
You can also see it in…
Infographics
Photo Gallery.

Video Gallery



