FAQs about Hurricanes
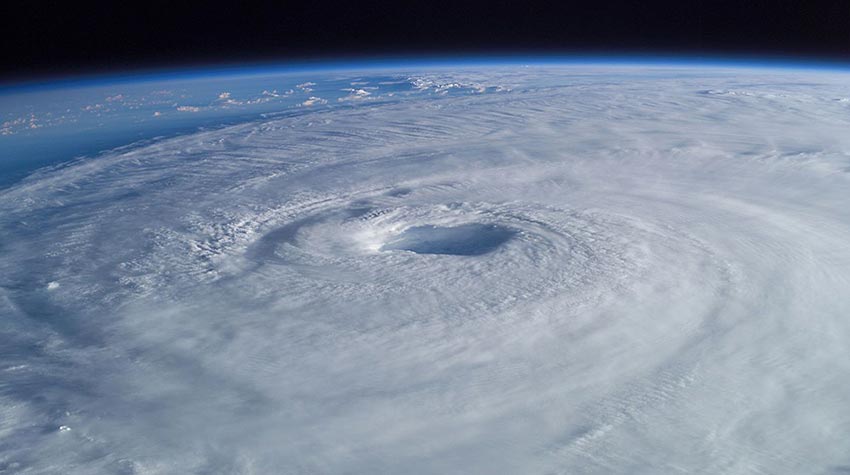

9. How are hurricanes measured?
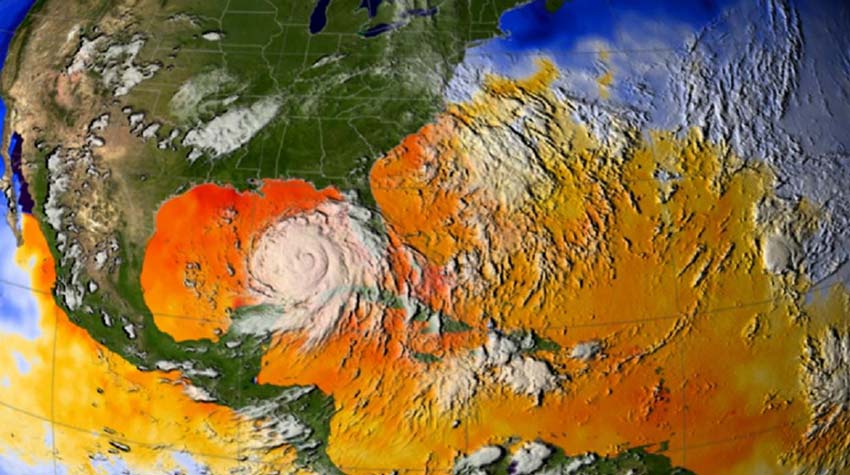
To measure the speed of a hurricane, “hurricane hunter” aircraft are used, whose pilots travel to the eye of the hurricane and release small probes to make these measurements. NASA has aircraft with more than 28 hours of flight autonomy, which can rise up to 18 km in height. From that level down to the eye of the storm to release these devices. These, cylindrical in shape, about 30 cm long and 15 cm wide, can measure a series of values in addition to the temperature and intensity of the wind. These data are collected by equipment installed in the aircraft that are processing the data, sending it to the National Hurricane Center for publication and location on the Saffir-Simpson scale.
FAQs about Hurricanes
1. What are tropical cyclones?
2. What is a tropical depression?
3. What is a tropical storm?
4. What is a hurricane?
5. How do hurricanes form?
6. Is there any relationship between global warming and hurricanes?
7. What is the difference between a hurricane and a typhoon?
8. What changes in hurricane activity are expected by the end of the 21st century?
9. How are hurricanes measured?
10. What is the Saffir-Simpson scale?
11. What are the five categories of hurricane intensity?
12. How are the names of the hurricanes chosen?
13. What have been the most devastating hurricanes?
14. What is the origin of the word “hurricane”?
15. What is the first story of a hurricane?
Other sections of Hurricanes
Article
What are hurricanes and how do they relate to global warming
There are mixed views on the relationship between global warming and hurricanes. So far, no evidence has been found to support this relationship. Whenever there is an extraordinary phenomenon that is supposed to be related to climate change, a precedent occurs, often 50, 100 or more years ago, when global warming, the main factor in climate change, was not a issue. However, with the recent Hurricane Irma (Sep-2017), there was a fact that had never happened. For the first time a cyclone acquired category 5 in the Atlantic Ocean, before reaching the Caribbean…
Magazine
Hurricanes, winds that cause great damage
A hurricane is a cyclone of great force that forms a whirlwind and turns in large circles. For a cyclone to be classified as a hurricane it must at least have a rotation speed of 119 km / h or 74 mps. A hurricane usually originates in the tropics and since its formation, in most cases, begins to expand its diameter and speed. Hurricanes are classified according to the Saffir Simpson wind scale, in five categories, mainly according to their speed…
You can also see it in…
Infographics
Photo Gallery.

Video Gallery



