FAQs about Wildfires

4. Are wildfires a cause or consequence of global warming?
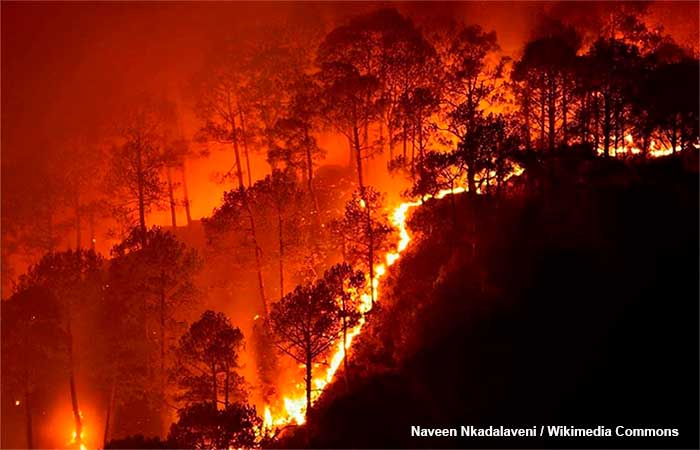
Wildfires are both, a cause, and a consequence of global warming, that is, they have a double effect on the increase in the planet’s temperature, measured since 1750.
Global warming as a cause of wildfires
Scientists claim that the main cause of wildfires is increased global warming. Warmer air causes drought, which makes trees and other plants burn more easily.
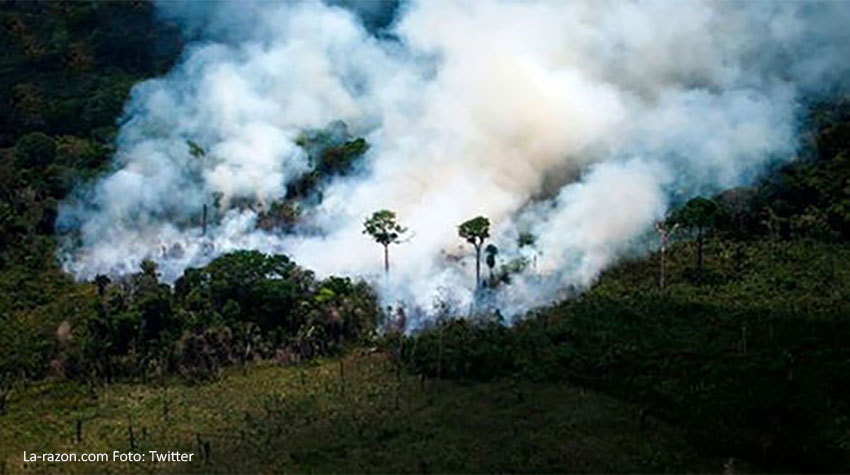
The large forest fires that have occurred in California, United States, in recent years were in the fall after long and hot summers that absorbed moisture from the vegetation before the rains began. Extreme drought turns all dry material into an easy-to-ignite fuel with the slightest induction. Due to delayed rainfall in recent decades, the fire season has been extended by 75 days. The dry seasons, coupled with the seasonal winds, have made the flames spread strongly and control them difficult.
Likewise, experts assure that the main cause of the fires in Australia is due to global warming, which in 2019 marked record temperatures, with an annual average of almost 42 degrees Celsius and peaks close to 50 degrees Celsius.
Global warming as a consequence of wildfires
Wildfires, on the one hand, send large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere increasing the amount of PPM of CO2, Parts Per Million of CO2, cause of global warming. But, on the other hand, destroying trees and other plants reduces the carbon sink effect, that is, they absorb and store CO2. Plants, although they take oxygen from the air and re-enter CO2, the bottom line is positive in terms of the extraction of CO2 from the atmosphere.
The CO2 absorption capacity is directly proportional to the size, density and quantity of trees present in a forest. In a mega forest fire are tens of thousands of trees that go out of play. As a consequence, the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere and the heat on the planet increases.
FAQs about Wildfires
1. What is a wildfire, and which are the most affected countries?
2. What are the causes of wildfires?
3. What are the consequences of wildfires?
4. Are wildfires a cause or consequence of global warming?
5. What is the relationship between deforestation and forest fires?
6. Why is it difficult to regulate the deforestation of forests?
7. How is biodiversity affected by forest fires?
8. How does smoke from fires affect air pollution?
Other sections of Wildfires
Articles
It is no little that is at stake in the Amazon rainforest. The lung of the world should not be a token in a casino roulette. This biodiversity emporium is about 7 million km2, it is 12 times the size of Spain, it has 80,000 kinds of trees, 140,000 species of plants, 20% of the world’s species. Keep reading…
And you can also see it in…
Infographics
Photo Gallery

Video gallery



