Special Report 2021
Green Hydrogen
The purpose of this report is to update the reader about the present and future of the green hydrogen.
Will green hydrogen be the fuel of the future?
The hydrogen atom is the simplest and most abundant in the universe.
It has only one electron and therefore ranks number one on the periodic table.
“Hydrogen is, in many ways, the perfect fuel. It is the most efficient and the cleanest burning. Hydrogen can produce electricity and this, in turn, can generate hydrogen, thus creating a renewable and environmentally friendly energy loop.”
Metallic Carbides
First airplane powered entirely by green hydrogen

“Airbus has revealed three concepts for the world’s first zero-emission commercial aircraft which could enter service by 2035. These concepts each represent a different approach to achieving zero-emission flight, exploring various technology pathways and aerodynamic configurations in order to support the company’s ambition of leading the way in the decarbonisation of the entire aviation industry. All of these concepts rely on hydrogen as a primary power source…” According the Airbus Page.

Black hydrogen is made from oil or coal through a process that sends carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
Blue hydrogen, the most used for now, comes from natural gas, but greenhouse gases are also released during the method.
Green H2 is extracted from the water by electrolysis, a 100% clean procedure, but for now very expensive.
How many kind of hydrogen are there?
The designations black hydrogen, blue hydrogen and green hydrogen are intended to indicate the different processes from which H2 has been obtained, since there is only one type of hydrogen. The H atom is the simplest in the universe, it has a single electron and therefore ranks number one on the periodic table.
Black hydrogen is made from oil or coal through a process that sends carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Blue hydrogen, the most widely used for now, is derived from natural gas, but greenhouse gases are also released during the method. Green H2 is extracted from the water by electrolysis, a 100% clean procedure, but for now very expensive.
What is the purpose to produce Green Hydrogen?

Green hydrogen (H2) is the one obtained mainly through electrolysis. By means of this electrochemical method, the H2 of a water molecule (H2O) separates that of oxygen to obtain free H2.
The objective of producing green H2 is to obtain a completely clean, efficient and 100% sustainable fuel.
During the electrolysis process only water vapor is released. The electricity needed by the electrolyzers is generated by renewable sources such as solar energy, wind energy or hydraulic energy.
The use of green H2 will play a fundamental role in the coming years in the fight against climate change, by decarbonizing the planet. Green H2 will help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thereby helping to slow down the progressive increase in the Earth’s temperature.
But… the question is not as simple as it seems
The problem is that hydrogen (H2), being the most abundant element in the universe, is very rare to find it in a free state on Earth. This is because being the lightest element No. 1 in the periodic table, and consequently the lightest, it easily escapes the planet’s gravity, because the Earth does not have enough strong to hold it.
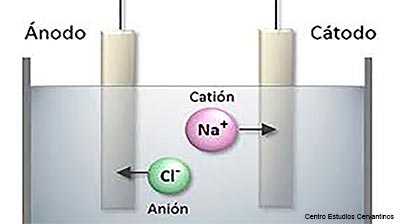
How to do in this case?
There are two methods to obtain it: one is by extracting the H2 from natural gas, oil or coal. But this has the disadvantage that during the process CO2 is released. The other is based on electrolysis, an electrochemical method, by which H2 is separated from oxygen in a water molecule (H2O). With this technology a 100% sustainable fuel is obtained, but it is very expensive. Only after making its production cheaper will green H2 be able to compete with fossil fuels.
According to the International Energy Agency, a Kilogram of green hydrogen has a price ranging from € 3.50 to € 5. Until the price is lowered to $ 2 or less, oil will continue to be the cheapest fuel source.
A global alliance to lower the cost of green hydrogen
Hydrogen is an unlimited resource, but despite being the most abundant element in the universe, on Earth it is very rare to find it in a free state. Obtaining free hydrogen corresponds to a very expensive process, which makes it uncompetitive compared to other fuels. The good news is that seven of the world’s leading companies have joined in a global coalition that will “accelerate the scale and production of green hydrogen over the next six years, helping to transform the most carbon-intensive industries, including power generation, chemicals, steelmaking and shipping. The initiative aims to reduce costs to less than $ 2 / Kg ”, as reported by the UN. An important step to leave the oil era behind.
Different uses of hydrogen



The “Green Hydrogen Catapult” coalition, the hope of a decarbonized world
On December 8, 2020, seven leading global companies announced the formation of a global coalition that will accelerate the scale and production of green hydrogen fifty times in the next six years, helping to transform the world’s most carbon-intensive industries, including generation energy, chemicals, steelmaking, air transportation and shipping.

The initiative, dubbed “Green Hydrogen Catapult” is formed by the leaders of the green hydrogen industry, including ACWA Power, CWP Renewables, Envision, Iberdrola, Ørsted, Snam and Yara, aiming at the deployment of 25 gigawatts until 2026 of hydrogen production based on renewable energies, with a view to reducing the cost of hydrogen to less than $ 2 US / Kg. According to information from the UN.
Could Green Hydrogen replace Solar Power and Wind Power?



Definitely not. First of all, solar and wind energy are for use in the home, business, health, education, etc. But they are also necessary during the electrolysis process so that the hydrogen obtained is 100% sustainable.
Second, hydrogen is used to supply electricity to heavy industries such as steel industry, maritime and air transport, which operate with high energy consumption. In short, green hydrogen does not compete with solar or wind energy, but with oil, natural gas and coal. For all this, the three sources of energy will play a crucial role in the decarbonization of the planet.
Climate Conferences Center
Exclusive of SGK PLANET

*COP21 *COP22 *COP23
*COP 24 *COP25 *COP26
*STOCHOLM 72 *RIO 92
*KYOTO 2007 *PARIS 2015
Frequently Asked Questions – Infographics
Articles – Image Gallery – Video Gallery
What happened at the COPs prior to COP26?
Brief History of COP ©
©First published November 2015 – Updated March 2023
Did you know that COPs originated in the Second Earth Summit, Rio de Janeiro 1992?
Here we present a summary of the first 25 COPs, with a short story and analysis of each one






















